What Is the Cost to Rewire a House?
Updating the wiring in a house could cost between $6 and $10 per square foot, but keeping old wiring could have disastrous consequences. Electrical issues are the third most common cause of house fires in the United States. Modern technology also may demand rewiring a house. Powering multiple electronic devices, having adequate interior and exterior lighting, and heating and cooling a home to today’s standards are difficult if a home’s electrical system is not up to the task. Given all this, rewiring is a common way to upgrade your home. Let’s explore what’s involved and how much is it to rewire a house.
Table of Contents
Key Points
• Rewiring costs for a house typically range from $6 to $10 per square foot.
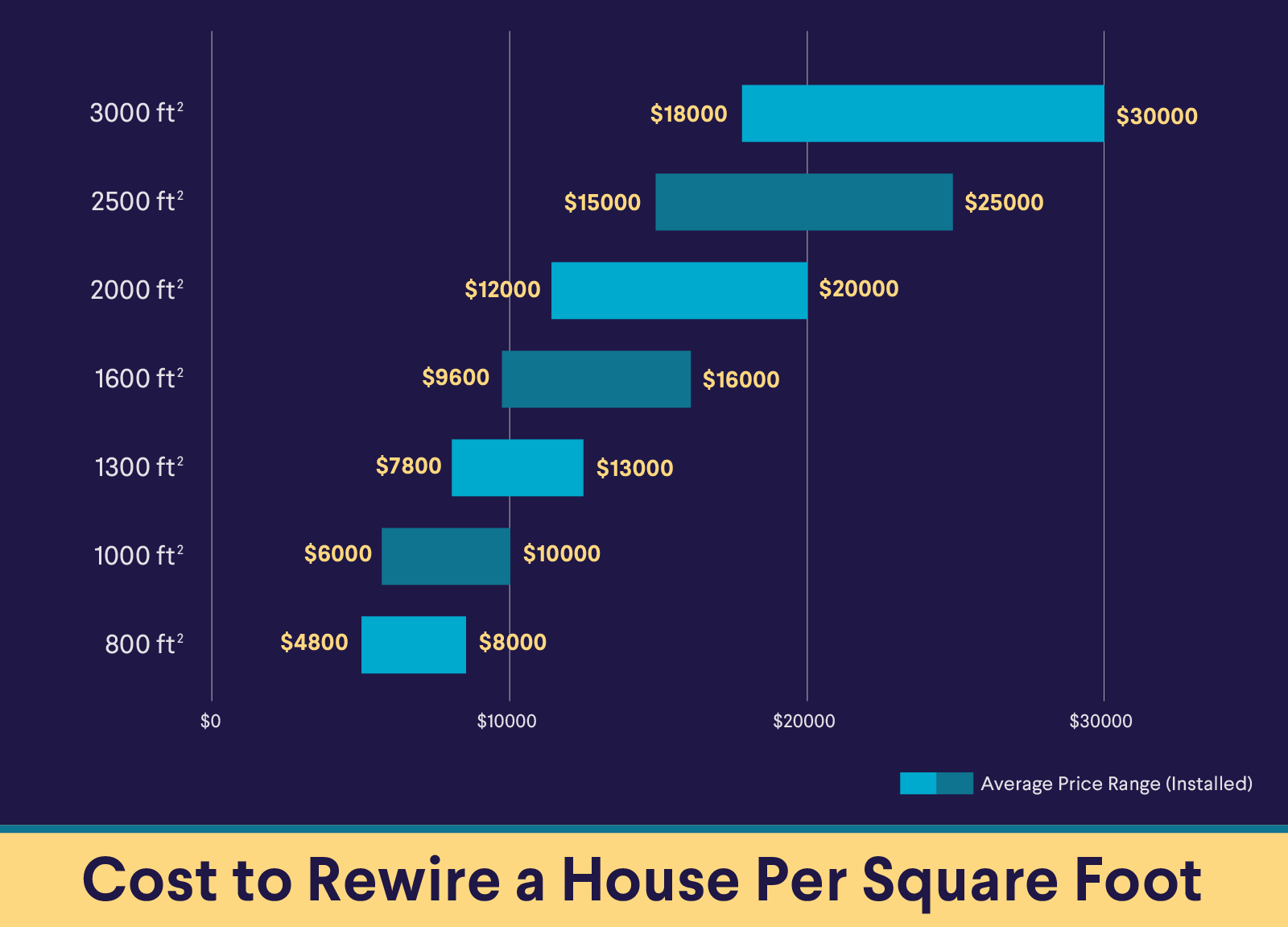
• A 1,300-square-foot house may cost between $7,800 and $13,000 to rewire.
• Rewiring a 2,500-square-foot home could range from $15,000 to $25,000.
• Factors influencing rewiring costs include house size, age, work extent, materials used, and wiring access.
• Older and larger homes often require more extensive rewiring, increasing the overall cost.
Factors That Affect the Cost to Rewire a House
Rewiring a home involves removing the outdated wiring inside a home’s walls and installing new, modern wiring that can safely meet today’s electrical needs.
Rewiring is typically done by a licensed electrician who strips out the old wiring and runs new wiring throughout the entire house, installs a new circuit breaker panel to handle the load of the new wiring system, and ensures that building codes are met.
It can be a big job — and an expensive one, too. Let’s look at some common factors that can impact the total cost.
Size of the House
The bigger the home, the more materials and labor the job will likely require. And that can drive up the price. Rewiring a 1,300-square-foot house, for instance, runs around $7,800 to $13,000. For a 2,500-square-foot home, you can expect to pay between $15,000 to $25,000.
House’s Age
Older homes weren’t constructed with 21st century living in mind, so a rewiring project will likely cost more. Common necessities like opening a wall to reach out-of-the-way wiring ($4-$8 per square foot), upgrading outdated wiring ($200-$2,300), and replacing an electrical outlet ($125-$200) can all add to the price tag.
Extent of Work Needed
Small-scale projects are typically cheaper than larger, more complex ones. If you’re planning to set up a new alarm system, run wiring to a backyard shed, or upgrade the electric panel, you’ll likely need to adjust your budget accordingly.
Type of Wiring and Materials Used
The average cost to rewire a house is just that: average. And your own house rewire costs will vary based on the materials used in the job. Below we’ll get into the details of how different materials can affect your job costs.
Local Labor Rates and Permit Requirements
If you’re in a high cost of living area, you can expect hourly rates for electricians, drywall repair, and painting to be above national averages. This, too, will affect the cost of your job.
Recommended: How to Find a Contractor for Home Remodeling
Signs You Need to Rewire a Home
Flickering lights, outlets making a popping sound, or tripped breakers indicate that a home might need to be rewired. When buying an older home, a home inspection typically reveals if rewiring is recommended or necessary.
Even before a professional inspection, prospective homebuyers may be able to get a good idea of how the home is wired by peeking into the attic, basement, or crawl space.
Vintage charm does not extend to knob and tube wiring, which was common through the mid-1900s. The lack of a ground wire is seen as a significant fire hazard, and most carriers will deny homeowners insurance for a home that has knob and tube electrical wiring.
Another way to check for outdated wiring is to find the electrical panel and see if it has modern breaker switches or round fuses. The fuses indicate that the system is outdated, and rewiring the house might be recommended.
In almost every state, home sellers must disclose defects, but cautious buyers may still want to include the inspection contingency in the purchase contract.
If you’re living in a home with older wiring and notice that your circuit breakers trip often, lights flicker, the light switches feel warm to the touch, or there is a burning smell coming from an outlet, it’s time to schedule an appointment with an electrician and explore house rewire costs. Get ready to encounter one of the more common home repair costs
What’s Involved in the Rewiring Process?
Rewiring a house can be a costly endeavor in part because it is a complex process. After all, most of those wires are inside your walls. Depending on the extent of the job, rewiring could involve any or all of the following: Replacing or adding circuits; running new wire through walls, ceiling, and floors; replacing (and potentially adding) outlets and switches; installing ground fault circuit interrupters, which are often required by building codes in areas with potential exposure to moisture such as kitchens and bathrooms. After the work is done, the electrical contractor will test the system.
Filing for building permits before the work and managing an inspection once it is done will also likely be necessary. And in some jobs, an electrical service upgrade will be needed to bring more power to the home. This adds to cost and complexity.
Now let’s look more closely at how much does it cost to rewire a home based on the type of materials being used.
Cost to Rewire a House Per Material
The cost of rewiring a house depends on square footage and how easy or difficult it is to access the space. But the wiring and cable materials can also have an impact. Let’s take a look:
• Used in most homes, nonmetallic (NM) cables are easy to install, flexible, and cost-effective. If you’re rewiring these cables, expect to pay between $0.40 and $0.80 per linear foot, according to Angi.
• Underground feeder (UF) cables are similar to NM cables, except that they’re designed to go underground or in damp areas. Rewiring UF cables costs around $0.50 to $0.75 per linear foot.
• Durable and able to handle high temperatures, THHN and THWN wires are often used in an unfinished space, like a basement, or for hot water heaters and garbage disposals. They cost $0.80 to $1.60 per linear foot to rewire.
• Coaxial cables have high bandwidth support and are easy to install, which once made them a go-to choice for televisions and video equipment. Today, they’re more commonly used to connect cable or satellite TV signals or for internet connectivity. These cables cost around $0.25 to $0.35 per linear foot to rewire.
Updating a doorbell or thermostat? You’ll likely be working with low-voltage wires, which are used for circuits less than 50 volts. Rewiring typically costs between $0.25 and $0.35.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wiring
As you explore rewiring the house, you may find references to both aluminum and copper wire. If your home dates to the 1970s, it may have aluminum wiring, which was used often in that era because it was light and cheap. Unfortunately, it was also more prone than copper to oxidizing and expanding, which created hazards. Copper is the preferred material and what you will likely be upgrading to. Copper’s conductivity makes it highly efficient and a lower fire risk than aluminum.
Cost of Upgrading the Electrical Panel
If the wiring in your home is outdated, it is possible that your electrical panel will also need an update to provide the level of service necessary for the needs of a modern home. A basic panel upgrade can cost $2,000 to $4,000, with additional costs for a service upgrade requiring underground wiring, for example.
Additional Costs for Smart Home or Energy-Efficient Upgrades
These days, there are abundant add-ons for any wiring project. The universe of smart-home devices seems to be expanding exponentially. A basic smart-home upgrade for your home, often done alongside a rewiring job, might run you between $2,000 and $7,000. This would include installing a hub with a smart speaker and automated door locks, thermostat, and smart lighting in several rooms. If you go all in on a smart refrigerator and other gadgets, the price could climb as high as $16,000.
Recommended: How Much Is My House Worth?
Awarded Best Online Personal Loan by NerdWallet.
Apply Online, Same Day Funding
How to Cover Your House Rewiring Costs
Rewiring a home is not a small expense. Fortunately, there are several ways to pay for it. Here’s a look at some options.
Home Equity Loans
If you’ve built up equity in your home and are facing a major rewiring project, one possible solution is a home equity loan. There are three main types of home equity borrowing to consider: a fixed-rate home equity loan, a home equity line of credit (HELOC), and cash-out refinancing. All of these use your home as collateral, meaning that if you miss payments you could face foreclosure.
Each has its pros and cons. For instance, with a fixed-rate home equity loan, you receive a lump sum payment, which you’ll pay back over a period of time with a set interest rate.
A HELOC, on the other hand, is revolving debt. As the balance borrowed is paid down, it can be borrowed again during the draw period, which typically lasts 10 years. HELOCs tend to have a variable interest rate, so payments are less predictable.
With a cash-out refinance, you can refinance your mortgage for more than what you currently owe, and then take the difference in cash that you can use to cover your renovation.
Home Improvement Loans
A home improvement loan is a type of personal loan used to fund renovations and upgrades, including rewiring a house. Once your loan application is approved, you’ll receive a lump sum of cash, which you can use to pay for home improvements. You’ll repay the loan, with interest, in regular installments over the life of the loan — typically five to seven years.
These loans are unsecured, which means your home isn’t used as collateral. As a result, they often come with a higher interest rate than a home equity loan or HELOC.
💡 Quick Tip: Check out SoFi’s home improvement loan rates to explore competitive terms and find the right financing for your renovation needs.
Credit Cards
A credit card is a fast, easy way to fund a rewiring project, and it can be a good option if you’re able to pay off the balance on the card that month. Or look for a card with an introductory 0% annual percentage rate (APR), as this allows you anywhere from six to 18 months to pay back the balance with zero interest. But keep in mind that any balance left after the promotional period ends will start accruing the card’s regular APR.
Also watch for surcharges on credit card transactions. Many tradespeople charge fees for clients using credit cards, and these can quickly add a considerable sum to a larger project.
Government Assistance or Energy Efficiency Incentives
The U.S. Department of Energy provides tax credits and rebates for certain home energy projects, so it’s a good idea to check the DOE site to see what might be available when planning your project. Local governments and utility companies may also offer incentives if your project is considered energy efficient. The U.S. Department of Agriculture also provides grants and loans to qualified low-income households looking to make home improvements. And if you are purchasing a home that needs rewiring, you may be able to finance the purchase and renovation with an FHA 203(k) loan.
Cash
Depending on the scope of the project and your budget, you may decide to dip into your savings account or withdraw money from your emergency fund, if you have one, to cover the cost of rewiring a home.
As you create a budget and weigh your financing options, look for opportunities to save money. Research how much rewiring a house costs in your area, and include a cushion in your budget for unexpected expenses. If you’re not planning to tackle the job yourself, gather quotes from reputable licensed electricians in your area and see which one can offer you the best deal.
Finally, factor in the long-term costs and benefits. Although rewiring might seem cost-prohibitive when buying a single-family home, owners may find that the cost of rewiring a house — and the peace of mind the upgrade provides — can be money well spent.
Regardless of how you choose to pay for your rewiring job, it’s a good idea to track your home improvement costs, as these records may come in handy for tax purposes if you tackle home improvement projects to increase your home’s value before selling the property.
The Takeaway
At $6 to $10 per square foot, the cost of rewiring a house may seem high. But adequate electrical panels and modern wiring can amp up your home value and prevent fires. Wondering how you’re going to pay for it all? Home equity loans, savings, credit cards, and home improvement loans are all ways to pay for the average cost to rewire a house.
Think twice before turning to high-interest credit cards. Consider a SoFi personal loan instead. SoFi offers competitive fixed rates and same-day funding. See your rate in minutes.
FAQ
Is it worth rewiring an old house?
It’s not only worth rewiring an old house, it’s an important safety measure and a way of protecting your investment. Replacing outdated wiring can help prevent a house fire and add value to the property. Plus, updated, energy-efficient fixtures are sometimes included in a remodeling job of this scope, which can potentially lower utility costs.
How much does it cost to replace all the electrical wiring in a house?
According to the home services website Angi, home owners can expect to pay anywhere from $601 to $2,590 to rewire a house. However, if you have an older, larger home, you’ll likely pay closer to $6,000.
Can a house be rewired without removing drywall?
In many cases, at least some drywall or plaster will need to be removed during a rewiring project. But talk to your electrician to see if the work can be done without disrupting your walls.
What permits or inspections are needed to rewire a house?
All but the most minor electrical work typically requires a permit, although regulations are set locally so you’ll want to explore exactly what is required in your area. Rewiring a house is quite a big job and so any costs associated with permitting should be part of the electrician’s bid.
How long does it typically take to rewire a house?
Rewiring a house can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the size of the job. Angi reports an average time of three to 10 days, with longer times for older and larger houses. If rewiring is happening in the context of other renovations, such as an HVAC installation or plumbing work, you can expect it to take longer. Add additional time for replacing sheetrock or plaster that has been removed and repainting the affected area.
Photo credit: iStock/Dmitriev
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
¹FHA loans are subject to unique terms and conditions established by FHA and SoFi. Ask your SoFi loan officer for details about eligibility, documentation, and other requirements. FHA loans require an Upfront Mortgage Insurance Premium (UFMIP), which may be financed or paid at closing, in addition to monthly Mortgage Insurance Premiums (MIP). Maximum loan amounts vary by county. The minimum FHA mortgage down payment is 3.5% for those who qualify financially for a primary purchase. SoFi is not affiliated with any government agency.
²SoFi Bank, N.A. NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC), offers loans directly or we may assist you in obtaining a loan from SpringEQ, a state licensed lender, NMLS #1464945.
All loan terms, fees, and rates may vary based upon your individual financial and personal circumstances and state.You should consider and discuss with your loan officer whether a Cash Out Refinance, Home Equity Loan or a Home Equity Line of Credit is appropriate. Please note that the SoFi member discount does not apply to Home Equity Loans or Lines of Credit not originated by SoFi Bank. Terms and conditions will apply. Before you apply, please note that not all products are offered in all states, and all loans are subject to eligibility restrictions and limitations, including requirements related to loan applicant’s credit, income, property, and a minimum loan amount. Lowest rates are reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Products, rates, benefits, terms, and conditions are subject to change without notice. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria. Information current as of 06/27/24.In the event SoFi serves as broker to Spring EQ for your loan, SoFi will be paid a fee.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Disclaimer: Many factors affect your credit scores and the interest rates you may receive. SoFi is not a Credit Repair Organization as defined under federal or state law, including the Credit Repair Organizations Act. SoFi does not provide “credit repair” services or advice or assistance regarding “rebuilding” or “improving” your credit record, credit history, or credit rating. For details, see the FTC’s website .
Third Party Trademarks: Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards Center for Financial Planning, Inc. owns and licenses the certification marks CFP®, CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
This article is not intended to be legal advice. Please consult an attorney for advice.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
SOPL-Q126-001
Read more



