How Much Will a $350,000 Mortgage Cost You?
Over the life of a $350,000 mortgage with a 6.00% interest rate, borrowers could expect to pay from $155,682 to $347,515 in total interest, depending on whether they opt for a 15-year or 30-year loan term. But the actual cost of a mortgage depends on several factors, including the interest rate, and whether you have to pay private mortgage insurance.
Besides interest, homebuyers need to account for a down payment, closing costs, and the long-term costs of taxes and insurance policies that are included in a $350,000 mortgage payment.
Table of Contents
Key Points
• The total cost of a $350,000 mortgage can range from $2,000 to over $3,500 monthly, depending on the loan term and interest rate; the payment includes principal and interest, and possibly property taxes, mortgage insurance, and homeowners insurance.
• A longer 30-year term results in a lower monthly payment but more interest paid, while a shorter 15-year term results in a higher monthly payment but less than half the total interest paid.
• Homebuyers who make a down payment less than 20% usually have to pay for private mortgage insurance as part of their loan payment.
• Borrowers must account for upfront costs, including a down payment (typically 3% to 20%) and closing costs (2% to 5% of the loan principal).
• To afford a $350,000 mortgage with a $2,328 monthly payment, the 28/36 rule suggests a minimum gross annual income of about $96,600.
First-time homebuyers can
prequalify for a SoFi mortgage loan,
with as little as 3% down.
Questions? Call (888)-541-0398.
Cost of a $350,000 Mortgage
When you finance a home purchase, you have to pay back more than the borrowed amount, known as the loan principal. The total cost of taking out a $350,000 mortgage is about $757,000 with a 30-year term at a 6.00% interest rate. This comes out to around $405,900 worth of interest, assuming there aren’t any late monthly mortgage payments or pre-payments.
When you buy a home, there are usually some upfront costs you’ll have to pay, too. Mortgages often require a down payment, calculated as a percentage of home purchase price, that’s paid out of pocket to secure financing from a lender. The required amount varies by loan type and lender, but average down payments range from 3% to 20%.
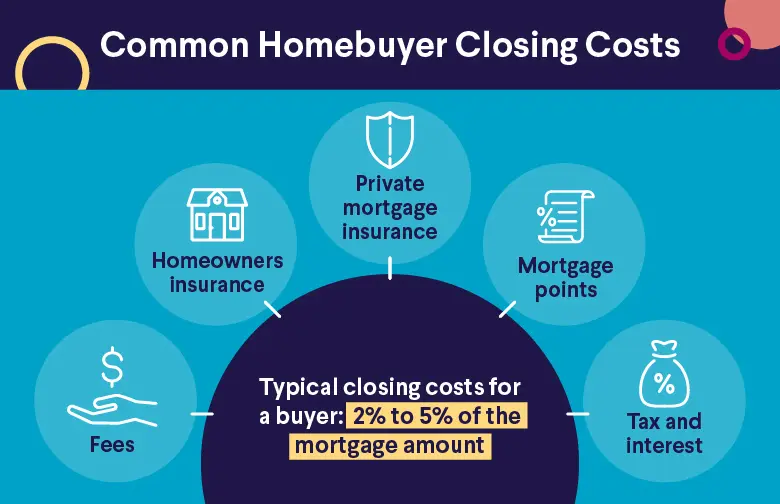
Closing costs, including home inspections, appraisals, and attorney fees, represent another upfront cost for real estate transactions. They typically sum up to 2% to 5% of the loan principal, or $10,500 to $21,000 on a $350,000 mortgage.
The total down payment on $350,000 mortgages also impacts the total cost of taking out a home loan. Unless buyers put 20% or more down on a home purchase, they’ll have to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI) with their monthly mortgage payment. The annual cost of PMI is generally between 0.5% – 1.5% of the loan principal. Borrowers can get out of paying PMI with a mortgage refinance or when they reach 20% equity in their home. If this is your first time in the housing market, consider reading up on tips to qualify for a mortgage.
💡 Quick Tip: When house hunting, don’t forget to lock in your home mortgage loan rate so there are no surprises if your offer is accepted.
Monthly Payments for a $350,000 Mortgage
The monthly payment on a $350K mortgage won’t be the same amount for every homeowner. You’ll need to factor in your down payment, interest rate, and loan term to estimate your $350,000 mortgage monthly payment.
With a 30-year loan term and 6.00% interest rate, borrowers can expect to pay around $2,100 a month. Whereas a 15-year term at the same rate would have a monthly payment of approximately $2,956. However, these estimates only account for the loan principal and interest. Monthly mortgage payments also include taxes and insurances, but these costs can differ considerably by location and based on a home’s assessed value.
There are also different types of mortgages to consider. Whether you opt for a fixed vs. adjustable-rate mortgage, for instance, will affect your monthly payment.
To get a clearer idea of what your monthly payment might be with different down payments and loan terms, try using a mortgage calculator.
Recommended: Best Affordable Places to Live in the U.S.
Where to Get a $350,000 Mortgage
Homebuyers have many options in terms of lenders, including banks, credit unions, mortgage brokers, and online lenders.
The homebuying process can be stressful, so it may be tempting to go with the first mortgage offer you receive. However, shopping around and getting loan estimates from multiple lenders lets you choose the one that’s the most competitive and cost-effective.
Even a fraction of a percentage point difference on an interest rate can add up to thousands in savings over the life of a mortgage. Besides the interest rate, assess the fees, terms, and closing costs when comparing mortgage offers.
Get matched with a local
real estate agent and earn up to
$9,500‡ cash back when you close.
Pair up with a local real estate agent through HomeStory and unlock up to
$9,500 cash back at closing.‡ Average cash back received is $1,700.
Recommended: Home Loan Help Center
What to Consider Before Applying for a $350,000 Mortgage
When taking out a mortgage, it’s important to consider the total cost of the loan. You’ll need cash on hand for a down payment and closing costs, plus sufficient income and funds to cover the monthly payment and other homeownership costs.
Before applying for a $350,000 mortgage, crunching the numbers in a housing affordability calculator can give a better understanding of how these costs will work with your finances.
It’s also helpful to see how $350,000 mortgage monthly payments are applied to the loan interest and principal over the life of the loan. The majority of the monthly mortgage payment goes toward interest rather than paying off the loan principal, as demonstrated by the amortization schedules below.
Here’s the mortgage amortization schedule for a 30-year $350,000 mortgage with a 7.00% interest rate — which would amount to $488,233 in interest. For comparison, we’ve also included the mortgage amortization schedule for a 15-year $350,000 mortgage with a 7.00% interest rate. A $350,000 mortgage payment, 15 years’ out, would add up to $216,229 in interest. When weighing a 30-year vs 15-year loan term, the shorter loan term carries a higher monthly payment but less than half the total interest over the life of the loan.
Amortization Schedule, 30-year Mortgage at 7.00%
| Year | Beginning Balance | Total Interest Paid | Total Principal Paid | Remaining Balance |
| 1 | $350,000 | $24,386 | $3,555 | $346,425 |
| 2 | $346,425 | $24,129 | $3,812 | $342,613 |
| 3 | $342,613 | $23,853 | $4,088 | $338,525 |
| 4 | $338,525 | $23,558 | $4,383 | $334,142 |
| 5 | $334,142 | $23,241 | $4,700 | $329,442 |
| 6 | $329,442 | $22,901 | $5,040 | $324,402 |
| 7 | $324,402 | $22,537 | $5,404 | $318,998 |
| 8 | $318,998 | $22,146 | $5,795 | $313,203 |
| 9 | $313,203 | $21,717 | $6,214 | $306,989 |
| 10 | $306,989 | $21,278 | $6,663 | $300,326 |
| 11 | $300,326 | $20,796 | $7,145 | $293,182 |
| 12 | $293,182 | $20,280 | $7,661 | $285,520 |
| 13 | $285,520 | $19,726 | $8,215 | $277,306 |
| 14 | $277,306 | $19,132 | $8,809 | $268,497 |
| 15 | $268,497 | $18,496 | $9,446 | $259,051 |
| 16 | $259,051 | $17,813 | $10,128 | $248,923 |
| 17 | $248,923 | $17,081 | $10,861 | $238,062 |
| 18 | $238,062 | $16,295 | $11,646 | $226,417 |
| 19 | $226,417 | $15,454 | $12,488 | $213,929 |
| 20 | $213,929 | $14,551 | $13,390 | $200,539 |
| 21 | $200,539 | $13,583 | $14,358 | $186,181 |
| 22 | $186,181 | $12,545 | $15,396 | $170,784 |
| 23 | $170,784 | $11,432 | $16,509 | $154,275 |
| 24 | $154,275 | $10,238 | $17,703 | $136,573 |
| 25 | $136,573 | $8,959 | $18,982 | $117,590 |
| 26 | $117,590 | $7,586 | $20,355 | $97,236 |
| 27 | $97,236 | $6,115 | $21,826 | $75,409 |
| 28 | $75,409 | $4,537 | $23,404 | $52,006 |
| 29 | $52,006 | $2,845 | $25,096 | $26,910 |
| 30 | $26,910 | $1,031 | $26,910 | $0 |
Amortization Schedule, 15-year Mortgage at 7.00%
| Year | Beginning Balance | Total Interest Paid | Total Principal Paid | Remaining Balance |
| 1 | $350,000 | $24,065 | $13,684 | $336,296 |
| 2 | $336,296 | $23,076 | $14,673 | $321,624 |
| 3 | $321,624 | $22,015 | $15,733 | $305,890 |
| 4 | $305,890 | $20,878 | $16,871 | $289,020 |
| 5 | $289,020 | $19,658 | $18,090 | $270,929 |
| 6 | $270,929 | $18,351 | $19,398 | $251,531 |
| 7 | $251,531 | $16,948 | $20,800 | $230,731 |
| 8 | $230,731 | $15,445 | $22,304 | $208,427 |
| 9 | $208,427 | $13,832 | $23,916 | $184,510 |
| 10 | $184,510 | $12,103 | $25,645 | $158,865 |
| 11 | $158,865 | $10,249 | $27,499 | $131,366 |
| 12 | $131,366 | $8,261 | $29,487 | $101,879 |
| 13 | $101,879 | $6,130 | $31,619 | $70,260 |
| 14 | $70,260 | $3,844 | $33,904 | $36,355 |
| 15 | $36,355 | $1,393 | $36,355 | $0 |
Recommended: The Cost of Living By State
How to Get a $350,000 Mortgage
To qualify for a $350,000 mortgage, borrowers will need to meet the income, credit, and down payment requirements. It’s also important to have an adequate budget for long-term housing costs and other financial goals and obligations like savings and debt.
Using the 28/36 rule, a monthly mortgage payment shouldn’t be more than 28% of your monthly gross income and 36% of your total debt to be considered affordable. With a $2,328 monthly mortgage payment, you’d need a minimum gross monthly income of at least $8,300, or annual income of $96,600, to follow the 28% rule. Similarly, your total debt could not exceed $660 to keep housing and debt costs from surpassing 36%.
Home mortgage loans, with the exception of certain government-backed loans, require a minimum credit score of 620 to qualify. However, a higher credit score can help secure more competitive rates. If you qualify as a first-time homebuyer, you could get a FHA loan with a credit score of 500 or higher, though borrowers with a credit score below 580 will have to make a 10% down payment.
As mentioned above, it’s a good idea to compare lenders and loan types to find the most favorable rate and loan terms. From there, getting preapproved for a home loan is a logical next step to determine the loan amount and interest rate you qualify for. It also puts you in a better position to demonstrate you’re a serious buyer when making an offer on a property.
After putting in an offer, completing the mortgage application requires many of the same forms used for preapproval, plus an earnest money deposit.
💡 Quick Tip: Generally, the lower your debt-to-income ratio, the better loan terms you’ll be offered. One way to improve your ratio is to increase your income (hello, side hustle!). Another way is to consolidate your debt and lower your monthly debt payments.
The Takeaway
Buying a home is the largest purchase many Americans make in their lifetime. How much you’ll end up paying for a $350,000 mortgage depends on the interest rate and loan term. On a $350,000 mortgage, the monthly payment can range from around $2,000 to $3,500 based on these factors.
Looking for an affordable option for a home mortgage loan? SoFi can help: We offer low down payments (as little as 3% - 5%*) with our competitive and flexible home mortgage loans. Plus, applying is extra convenient: It's online, with access to one-on-one help.
FAQ
How much is a $350K mortgage a month?
The cost of a $350,000 monthly mortgage payment is influenced by the loan term and interest rate. On a $350K mortgage with 7.00% interest, the monthly payment ranges from $2,328 to $3,146 depending on the loan term. The same loan with a 6.00% interest rate would cost around $2,100 to $3,000 per month.
How much income is required for a $350,000 mortgage?
Income requirements can vary by lender. But using the 28/36 rule, a borrower who isn’t burdened by lots of other debts should make $99,600 a year to afford the monthly payment on a $350,000 mortgage.
How much is a down payment on a $350,000 mortgage?
The down payment amount depends on the loan type and lender terms. FHA loans require down payments of 3.50% or 10.00%, while buyers could qualify for a conventional loan with as little as 3.00% down.
Can I afford a $350K house with a $70K salary?
It may be possible to afford a $350,000 house with a $70,000 salary, but only if you are able to make a sizable down payment to lessen the amount of money you need to borrow. Having a good credit score and minimal debt would also better your chances.
Photo credit: iStock/sturti
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
SoFi Mortgages
Terms, conditions, and state restrictions apply. Not all products are available in all states. See SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria for more information.
*SoFi requires Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) for conforming home loans with a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio greater than 80%. As little as 3% down payments are for qualifying first-time homebuyers only. 5% minimum applies to other borrowers. Other loan types may require different fees or insurance (e.g., VA funding fee, FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums, etc.). Loan requirements may vary depending on your down payment amount, and minimum down payment varies by loan type.
Up to $9,500 cash back: HomeStory Rewards is offered by HomeStory Real Estate Services, a licensed real estate broker. HomeStory Real Estate Services is not affiliated with SoFi Bank, N.A. (SoFi). SoFi is not responsible for the program provided by HomeStory Real Estate Services. Obtaining a mortgage from SoFi is optional and not required to participate in the program offered by HomeStory Real Estate Services. The borrower may arrange for financing with any lender. Rebate amount based on home sale price, see table for details.
Qualifying for the reward requires using a real estate agent that participates in HomeStory’s broker to broker agreement to complete the real estate buy and/or sell transaction. You retain the right to negotiate buyer and or seller representation agreements. Upon successful close of the transaction, the Real Estate Agent pays a fee to HomeStory Real Estate Services. All Agents have been independently vetted by HomeStory to meet performance expectations required to participate in the program. If you are currently working with a REALTOR, please disregard this notice. It is not our intention to solicit the offerings of other REALTORS. A reward is not available where prohibited by state law, including Alaska, Iowa, Louisiana and Missouri. A reduced agent commission may be available for sellers in lieu of the reward in Mississippi, New Jersey, Oklahoma, and Oregon and should be discussed with the agent upon enrollment. No reward will be available for buyers in Mississippi, Oklahoma, and Oregon. A commission credit may be available for buyers in lieu of the reward in New Jersey and must be discussed with the agent upon enrollment and included in a Buyer Agency Agreement with Rebate Provision. Rewards in Kansas and Tennessee are required to be delivered by gift card.
HomeStory will issue the reward using the payment option you select and will be sent to the client enrolled in the program within 45 days of HomeStory Real Estate Services receipt of settlement statements and any other documentation reasonably required to calculate the applicable reward amount. Real estate agent fees and commissions still apply. Short sale transactions do not qualify for the reward. Depending on state regulations highlighted above, reward amount is based on sale price of the home purchased and/or sold and cannot exceed $9,500 per buy or sell transaction. Employer-sponsored relocations may preclude participation in the reward program offering. SoFi is not responsible for the reward.
SoFi Bank, N.A. (NMLS #696891) does not perform any activity that is or could be construed as unlicensed real estate activity, and SoFi is not licensed as a real estate broker. Agents of SoFi are not authorized to perform real estate activity.
If your property is currently listed with a REALTOR, please disregard this notice. It is not our intention to solicit the offerings of other REALTORS.
Reward is valid for 18 months from date of enrollment. After 18 months, you must re-enroll to be eligible for a reward.
SoFi loans subject to credit approval. Offer subject to change or cancellation without notice.
The trademarks, logos and names of other companies, products and services are the property of their respective owners.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
¹FHA loans are subject to unique terms and conditions established by FHA and SoFi. Ask your SoFi loan officer for details about eligibility, documentation, and other requirements. FHA loans require an Upfront Mortgage Insurance Premium (UFMIP), which may be financed or paid at closing, in addition to monthly Mortgage Insurance Premiums (MIP). Maximum loan amounts vary by county. The minimum FHA mortgage down payment is 3.5% for those who qualify financially for a primary purchase. SoFi is not affiliated with any government agency.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Third Party Trademarks: Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards Center for Financial Planning, Inc. owns and licenses the certification marks CFP®, CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
Checking Your Rates: To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. However, if you choose a product and continue your application, we will request your full credit report from one or more consumer reporting agencies, which is considered a hard credit pull and may affect your credit.
SOHL-Q425-189
Read more