Home Equity Loans and HELOCs vs Cash-Out Refi
Home equity loans, home equity lines of credit (HELOCs), and cash-out refinances are all borrowing options that allow homeowners to access the equity they’ve built in their home. By tapping into home equity — the difference between a home’s current value and the amount still owed on the mortgage — homeowners can secure funds to meet other financial goals, such as making home improvements.
While these three types of loans do have similarities, there also are key differences in how each one works. Understanding the differences in a home equity loan vs. HELOC vs. cash-out refi can help you better determine which option is right for you.
Key Points
• Homeowners can access home equity through home equity loans, HELOCs, and cash-out refinancing for various financial goals.
• HELOCs provide a revolving line of credit with adjustable interest rates and a draw period.
• Cash-out refinancing replaces an existing mortgage, offering a lump sum with potentially lower interest rates.
• Home equity loans offer a lump sum with fixed interest rates, creating a second mortgage.
• Borrowing limits differ with HELOCs generally up to 90% equity, cash-out refinancing up to 80%, and home equity loans up to 85%.
Defining Home Equity Loans, HELOCs, and Cash-Out Refi
To start, it’s important to know the basic definitions of home equity loans, HELOCs, and cash-out refinances.
Home Equity Loan
A home equity loan allows a homeowner to borrow a lump sum that they’ll then repay over a set period of time in regular installments at a fixed interest rate. Generally, lenders will allow homeowners to borrow up to 85% of their home’s equity.
This loan is in addition to the existing mortgage, making it a second mortgage. As such, a borrower usually will make payments on this loan in addition to their monthly mortgage payments. To better understand what kind of payment might be due each month, it is helpful to use a home equity loan calculator.
HELOC
A HELOC is a line of credit secured by the borrower’s home that they can access on an as-needed basis, up to the borrowing limit. The amount of the line of credit is determined by the mortgage lender and based on the amount of equity a homeowner has built, though it can be up to 90% of the equity amount. Like a home equity loan, this is a second mortgage that a borrower assumes alongside their existing home loan.
How HELOCs work is somewhat like a credit card, in that it’s a revolving loan. For example, if a borrower is approved for a $30,000 home equity line of credit, they can access it when they want, for the amount they choose (though there may be a minimum draw requirement). The borrower is only charged interest on and responsible for repaying the amount they borrowed.
Another point that borrowers should keep in mind is that there is a draw period of 5 to 10 years, during which a borrower can access funds, and a repayment period of 10 to 20 years. During the draw period, the monthly payments can be relatively low because the borrower pays interest only. During the repayment period, on the other hand, the payments can increase significantly because both principal and interest have to be paid.
Cash-Out Refinance
A cash-out refinance is a form of mortgage refinancing that allows a borrower to refinance their current mortgage for more than what they currently owe in order to receive extra funds. With a cash-out refinance, the borrower’s current mortgage is replaced by an entirely new loan.
As an example, let’s say a borrower owns a home worth $200,000 and owes $100,000 on their mortgage at a high interest rate. They could refinance at a lower interest rate, while at the same time taking out a larger mortgage. For instance, they could refinance the mortgage at $130,000. In this case, $100,000 would replace the old mortgage, and the borrower would receive the remaining amount of $30,000 in cash.
Recommended: First-time Homebuyer Guide
First-time homebuyers can
prequalify for a SoFi mortgage loan,
with as little as 3% down.
Questions? Call (888)-541-0398.
Home Equity Loans and HELOCs vs. Cash-Out Refi
Here’s a look at how a home equity loan vs. HELOC vs. cash-out refinance stack up when it comes to everything from borrowing limit to interest rate to fees:
| Home Equity Loan | HELOC | Cash-Out Refinance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borrowing Limit | 85% of borrower’s equity | Up to 90% of borrower’s equity | 80% of borrower’s equity for most loans |
| Interest Rate | Fixed rate | Generally variable | May be fixed or variable |
| Type of Credit | Installment loan: Borrowers get a specific amount of money all at once that they then repay in regular installments throughout the loan’s term (generally 5 to 30 years). | Revolving credit: Borrowers receive a line of credit for a specified amount and have a draw period (5 to 10 years), followed by a repayment period (10 to 20 years). | Installment loan: Borrowers receive a lump sum payment from the excess funds of their new mortgage, which has a new rate and repayment terms (generally 15 to 30 years). |
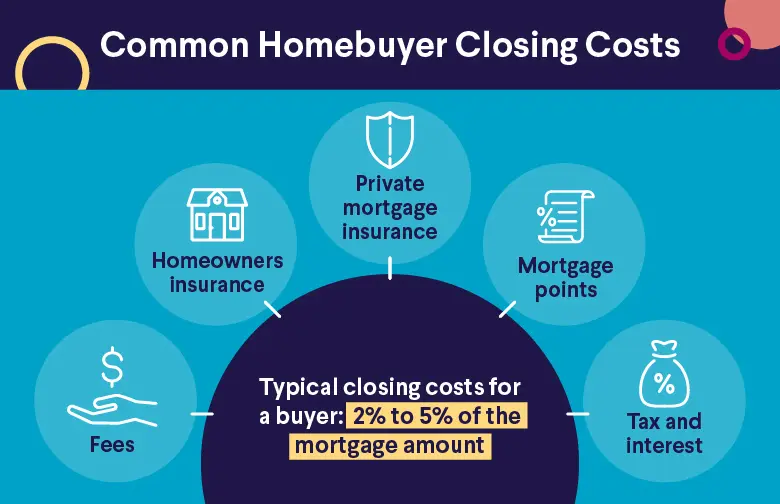
| Fees | Closing costs (typically 2% to 5% of the loan amount) | Closing costs (typically 2% to 5% of the loan amount), as well as other possible costs, depending on the lender (annual fees, transaction fees, inactivity fees, early termination fees) | Closing costs (typically 3% to 5% of the loan amount) |
| When It Might Make Sense to Borrow | Home equity loans can make sense for borrowers who want predictable monthly payments, or who want to consolidate higher interest debt. | HELOCs can be useful for situations where a borrower may want to access funds for ongoing needs over a specified period of time, or for borrowers funding a project, such as a renovation, where the cost is not yet clear. | Cash-out refinances may be useful if borrowers need a large sum of money, such as to pay off debt or finance a large home improvement project, and can benefit from a new interest rate and/or loan term. |
Borrowing Limit
With a home equity loan, lenders generally allow you to borrow up to 85% of a home’s equity. HELOCs allow borrowers to tap a similar amount, sometimes as much as 90%. Cash-out refinances, on the other hand, have a slightly lower borrowing limit — up to 80% of a borrower’s equity. The exception is a VA cash-out refi; here it is possible to borrow up to 100% per VA rules, although some lenders may impose a lower ceiling.
Interest Rate
With a home equity line of credit, the interest rate is usually adjustable. This means the interest rate can rise, and if it does, the monthly payment can increase. Home equity loans, meanwhile, generally have a fixed interest rate, meaning the interest rate remains unchanged for the life of the loan. This allows for more predictable monthly payment amounts.
A cash-out refinance can have either a fixed rate or an adjustable rate. Homeowners who opt for an adjustable rate may be able to access more equity overall.
Type of Credit
Both home equity loans and cash-out refinances are installment loans, where you receive a lump sum that you’ll then pay back in regular installments. A HELOC, on the other hand, is a revolving line of credit. This allows borrowers to take out and pay back as much as they need at any given time during the draw period.
Fees
With a home equity loan, HELOC, or cash-out refinance, borrowers may pay closing costs. HELOC closing costs may be lower compared to a home equity loan, though borrowers may incur other costs periodically as well, such as annual fees, charges for inactivity, and early termination fees.
When It Might Make Sense to Borrow
A home equity loan vs. HELOC vs. cash-out refi have varying use cases. With a fixed interest rate, home equity loans can allow for predictable payments. Their lower interest rates can make them an option for borrowers who want to consolidate higher interest debt, such as credit card debt.
HELOCs, meanwhile, provide more flexibility as borrowers can take out only as much as they need, allowing borrowers to continually access funds over a period of time. A cash-out refinance can be a good option for a borrower who wants to receive a large lump sum of money, such as to pay off debt or finance a large home improvement project.
Which Option Is Better?
Like most things in the world of finance, the answer to whether a cash-out refinance vs. HELOC vs. home equity loan is better will depend on a borrower’s financial circumstances and unique needs.
In all cases, borrowers are borrowing against the equity they’ve built in their home, which comes with risks. If a borrower is unable to make payments on their HELOC or cash-out refinance or home equity loan, the consequence could be selling the home or even losing the home to foreclosure.
Scenarios Where Home Equity Loans Are Better
A home equity loan can be the right option in certain scenarios, including when:
• You want fixed, regular second mortgage payments: A home equity loan generally will have a fixed interest rate, which can be helpful for budgeting as monthly payments will be more predictable. Some may appreciate this regularity for their second monthly mortgage payment.
• You want to get a lump sum while keeping your existing mortgage intact: Unlike a HELOC, where you draw just as much as you need at any given time, a home equity loan gives you a lump sum all at once. Plus, unlike a cash-out refinance, you aren’t replacing your existing mortgage. That way, if the terms of your current mortgage are favorable, those can remain as is.
Recommended: The Different Types Of Home Equity Loans
Scenarios Where HELOCs Are Better
In the following situations, a HELOC may make sense:
• You have shorter-term or specific needs: Because HELOCs generally have a variable interest rate, they can be useful for shorter-term needs or for situations where a borrower may want access to funds over a certain period of time, such as when completing a home renovation.
• You want the option of interest-only payments: During the draw period, HELOC lenders often offer interest-only payment options. This can help keep costs lower until the repayment period, when you’ll need to make interest and principal payments. Plus, you’ll only make payments on the balance used. A HELOC interest-only repayment calculator can help borrowers understand what those monthly payments might be.
Scenarios Where Cash-Out Refi Is Better
Cash-out refinances can make sense in these scenarios:
• You need a large sum of money: If there’s a need for a large sum of money, or if the funds can be used as a tool to improve your financial situation on the whole, a cash-out refinance can make sense.
• You can get a lower mortgage rate than you currently have: If refinancing can allow you to secure a lower interest rate than your current mortgage offers, then that could be a better option than taking on a second mortgage, as you would with a home equity loan or HELOC. If interest rates have risen since you first took out your loan, however, a cash-out refi could mean paying more in interest over the life of the loan.
• You want just one monthly payment: Because a cash-out refinance replaces your existing mortgage, you won’t be adding a second monthly mortgage payment to the mix. This means you’ll have only one monthly payment to stay on top of.
• You have a lower credit score but still want to tap your home equity: In general, it’s easier to qualify for a cash-out refinance vs. HELOC or home equity loan since it’s replacing your primary mortgage.
The Takeaway
Cash-out refinancing, HELOCs, and home equity loans each have their place in a borrower’s toolbox. All three options give borrowers the ability to turn their home equity into cash, which can make it possible to achieve important goals, consolidate debt, and improve their overall financial situation.
Homeowners interested in tapping into their home equity may consider getting a HELOC or taking a cash-out refinance with SoFi. Qualifying borrowers can secure competitive rates, and Mortgage Loan Officers are available to walk borrowers through the entire process.
FAQ
Can you take out a HELOC and cash-out refi?
If you qualify, it is possible to get both a HELOC and cash-out refinance. Qualified borrowers can use their cash-out refinance to help repay their HELOC.
Is it easier to qualify for a HELOC or cash-out refi?
It is generally easier to qualify for a cash-out refinance. This is because the cash-out refi assumes the place of the primary mortgage, whereas a HELOC is a second mortgage.
Can you borrow more with a HELOC or cash-out refi?
Ultimately, the amount you can borrow with either a cash-out refi or HELOC will depend on how much equity you have in your home. That being said, a HELOC can offer a slightly higher borrowing limit than a cash-out refi, at up to 90% of a home’s equity as opposed to a top limit of 80% for a cash-out refinance.
Are HELOCs or cash-out refi tax deductible?
Interest on your cash-out refinance or HELOC can be tax deductible so long as you use the funds for capital home improvements. This includes projects like remodeling and renovating.
SoFi Mortgages
Terms, conditions, and state restrictions apply. Not all products are available in all states. See SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria for more information.
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
*SoFi requires Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) for conforming home loans with a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio greater than 80%. As little as 3% down payments are for qualifying first-time homebuyers only. 5% minimum applies to other borrowers. Other loan types may require different fees or insurance (e.g., VA funding fee, FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums, etc.). Loan requirements may vary depending on your down payment amount, and minimum down payment varies by loan type.
²SoFi Bank, N.A. NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC), offers loans directly or we may assist you in obtaining a loan from SpringEQ, a state licensed lender, NMLS #1464945.
All loan terms, fees, and rates may vary based upon your individual financial and personal circumstances and state.You should consider and discuss with your loan officer whether a Cash Out Refinance, Home Equity Loan or a Home Equity Line of Credit is appropriate. Please note that the SoFi member discount does not apply to Home Equity Loans or Lines of Credit not originated by SoFi Bank. Terms and conditions will apply. Before you apply, please note that not all products are offered in all states, and all loans are subject to eligibility restrictions and limitations, including requirements related to loan applicant’s credit, income, property, and a minimum loan amount. Lowest rates are reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Products, rates, benefits, terms, and conditions are subject to change without notice. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria. Information current as of 06/27/24.In the event SoFi serves as broker to Spring EQ for your loan, SoFi will be paid a fee.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Checking Your Rates: To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. However, if you choose a product and continue your application, we will request your full credit report from one or more consumer reporting agencies, which is considered a hard credit pull and may affect your credit.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
This content is provided for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice.
SOHL-Q424-144
Read more