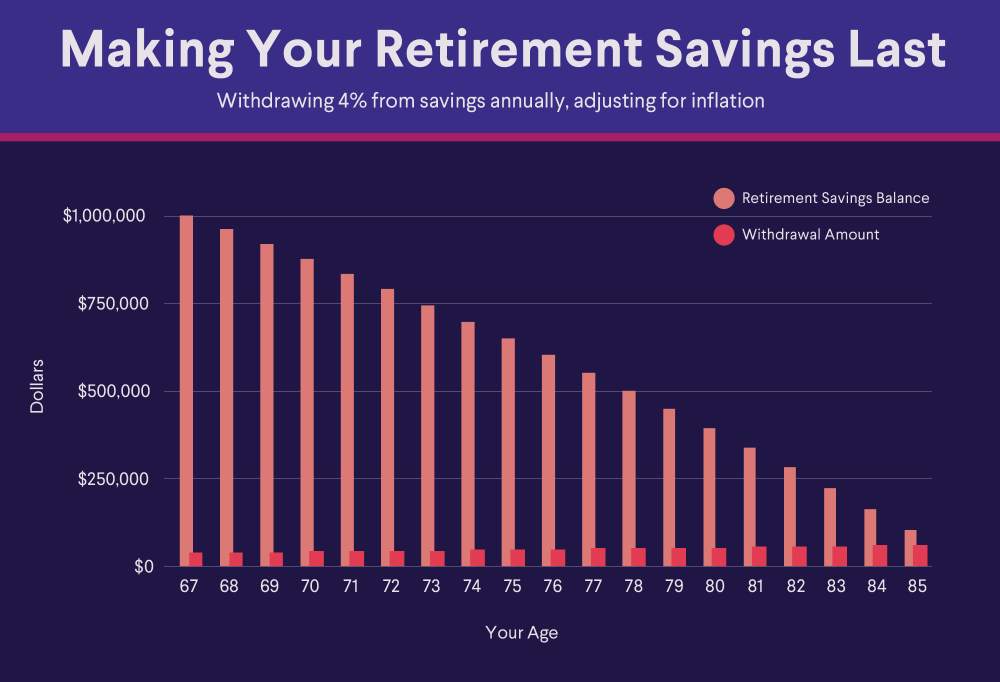
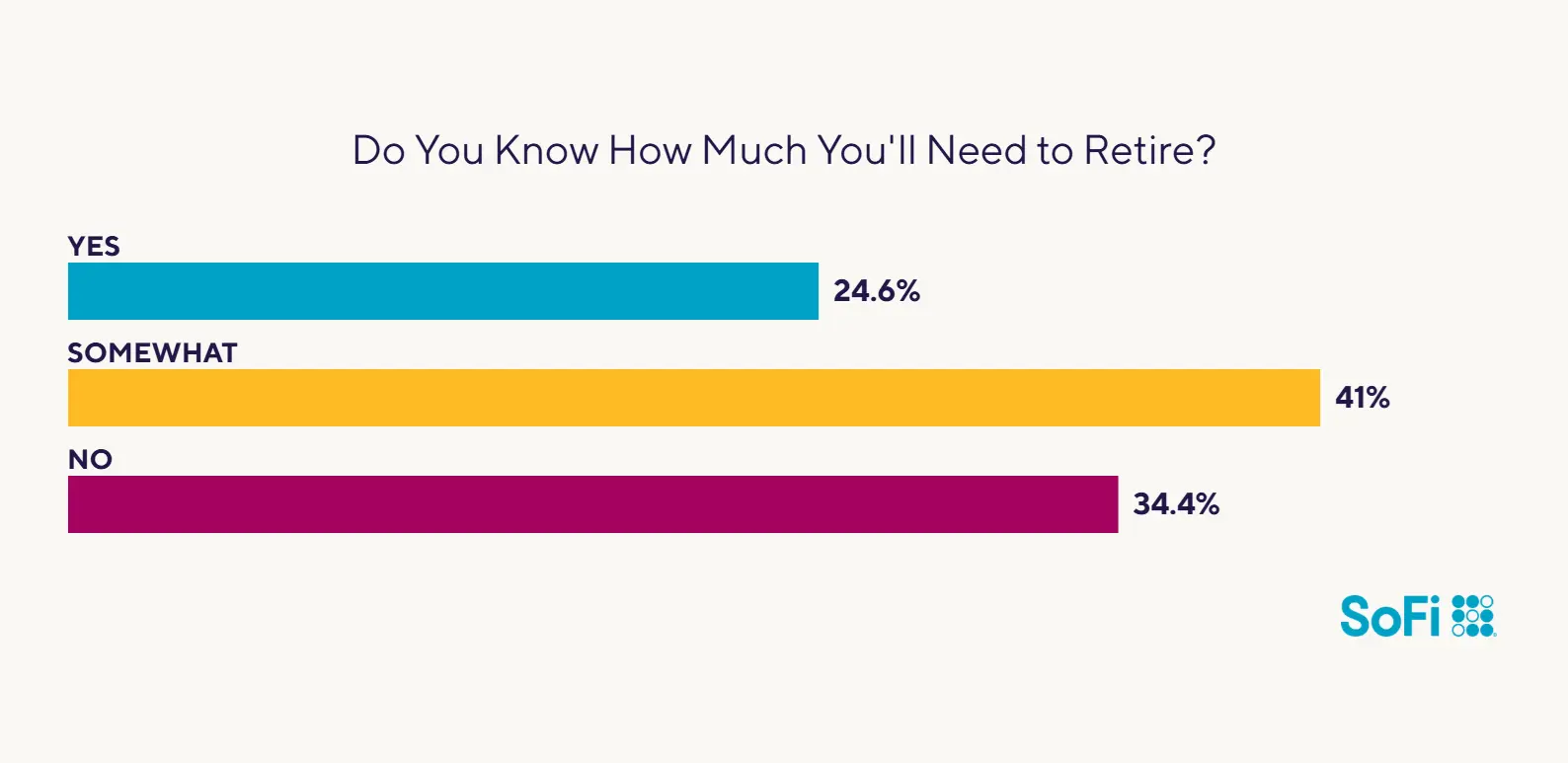What Is 401(k) Plan Benchmarking?
Table of Contents
Benchmarking a 401(k) retirement plan refers to how a company assesses their plan’s design, fees, and services to ensure they meet industry and ERISA (Employee Retirement Income Security Act) standards.
Benchmarking 401(k) plans is important for a few reasons. First, the company offering the plan needs to be confident that they are acting in the best interests of employees who participate in the 401(k) plan. And because acting in the best interests of plan participants is part of an employer’s fiduciary duty, benchmarking can help reduce an employer’s liability if fiduciary standards aren’t met.
If a company’s plan isn’t meeting industry benchmarks, it may be wise for an employer to change plan providers. Learn more about how benchmarking works and why it’s important.
Key Points
• Benchmarking evaluates 401(k) plan design, fees, and services to meet ERISA standards.
• Annual benchmarking can ensure compliance and help reduce employer liability.
• Administrative, investment, and transaction fees must be evaluated to make sure they are reasonable.
• Service quality of the plan, including customer support and investment guidance, is assessed.
• Optimizing 401(k) plan features may enhance employee retention and satisfaction.
How 401(k) Benchmarking Works
While a 401(k) plan is a convenient and popular way for participants to invest for retirement, the company offering the plan has many responsibilities to make sure that its plan is competitive. That is where 401(k) benchmarking comes into play.
An annual checkup is typically performed whereby a company assesses its plan’s design, evaluates fees, and reviews all the services offered by the plan provider. The 401(k) plan benchmarking process helps ensure that the retirement plan reduces the risk of violating ERISA rules. For the firm, a yearly review can help reduce an employer’s liability and it can save the firm money.
ERISA, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, requires that the plan sponsor verifies that the 401(k) plan has reasonable fees. ERISA is a federal law that mandates minimum standards that retirement plans must meet. It helps protect plan participants and beneficiaries.
The Importance of 401(k) Plan Benchmarking
It is important that an employer keep its 401(k) plan up to today’s standards. Making sure the plan is optimal compared to industry averages is a key piece of retirement benchmarking. It’s also important that your employees have a quality plan to help them save and invest for retirement. Most retirement plan sponsors conduct some form of benchmarking planning, and making that a regular event — such as annually — is important so that the employer continuously complies with ERISA guidelines.
Employers have a fiduciary responsibility to ensure that fees are reasonable for services provided. ERISA also states that the primary responsibility of the plan fiduciaries is to act in the best interest of their plan participants. 401(k) benchmarking facilitates the due diligence process and reduces a firm’s liability.
How to Benchmark Your 401(k) Plan: 3 Steps
So, as an employer, how exactly do you go about benchmarking 401(k) plans? There are three key steps that plan sponsors should take so that their liability is reduced, and the employees get the best service for their money. Moreover, 401(k) benchmarking can help improve your service provider to make your plan better.
1. Assess Your 401(k) Plan Design
It’s hard to know if your retirement plan’s design is optimal. Two gauges used to figure its quality are plan asset growth and the average account balance. If workers are continuously contributing and investments are performing adequately compared to market indexes, then those are signs that the plan is well designed.
Benchmarking can also help assess if a Roth 401(k) feature should be added. Another plan feature might be to adjust the company matching contribution or vesting schedule. Optimizing these pieces of the plan can help retain workers while meeting ERISA requirements.
2. Evaluate Your 401(k) Plan Fees
A 401(k) plan has investment, administrative, and transaction fees. Benchmarking 401(k) plan fees helps ensure total costs are reasonable. It can be useful to take an “all-in” approach when assessing plan fees. That method can better compare service providers since different providers might have different terms for various fees.
But simply selecting the cheapest plan does not account for the quality and depth of services a plan renders. Additional benchmarking is needed to gauge a retirement plan’s quality. Here are the three primary types of 401(k) plan fees to assess:
• Administrative: Fees related to customer service, recordkeeping, and any legal services.
• Investment: Amounts charged to plan participants and expenses related to investment funds.
• Transaction: Fees involved with money movements such as loans, 401(k) withdrawals, and advisory costs.
3. Evaluate Your 401(k) Provider’s Services
There are many variables to analyze when it comes to 401(k) benchmarking of services. A lot can depend on what your employees prefer. Reviewing the sponsor’s service model, technology, and execution of duties is important.
Also, think about it from the point of view of the plan participants: Is there good customer service available? What about the quality of investment guidance? Evaluating services is a key piece of 401(k) plan benchmarking. A solid service offering helps employees make the most out of investing in a 401(k) account.
The Takeaway
Investing for retirement is more important than ever as individuals live longer and pension plans are becoming a relic of the past. With today’s technology, and clear rules outlined by ERISA, it may be easier for workers to take advantage of high-quality 401(k) plans to help them save and invest for the long term.
For the company offering the plan, establishing a retirement benchmarking process is crucial to keeping pace with the best 401(k) plans. Reviewing a plan’s design, costs, and services helps workers have confidence that their employer is working in their best interests. Benchmarking can also protect employers.
If your company already has a 401(k) plan that you contribute to as an employee, you might also consider other individual retirement accounts to open. You can learn more about various options available, such as IRAs. There are different types of IRAs, including traditional and Roth IRAs. You may want to explore them as an option to help reach your retirement savings goals.
Prepare for your retirement with an individual retirement account (IRA). It’s easy to get started when you open a traditional or Roth IRA with SoFi. Whether you prefer a hands-on self-directed IRA through SoFi Securities or an automated robo IRA with SoFi Wealth, you can build a portfolio to help support your long-term goals while gaining access to tax-advantaged savings strategies.
Help build your nest egg with a SoFi IRA.
FAQ
How often should a 401(k) be benchmarked?
It’s considered a best practice to benchmark a 401(k) annually to make sure the plan complies with ERISA (Employee Retirement Income Security Act) guidelines. Making sure that the plan’s fees are reasonable and acting in the best interests of plan participants is part of an employer’s fiduciary duty. Benchmarking facilitates the due diligence process and reduces an employer’s liability if fiduciary standards aren’t met.
How do I benchmark my 401(k) fees?
To benchmark your 401(k) fees, take an “all-in” approach by calculating the service provider fees plus the investment expenses for the plan. This helps you compare your plan’s fees to fees charged by other service providers. In addition, assess the plan’s quality by looking at administrative fees (fees related to customer service and recordkeeping, for instance), investment fees (expenses related to investment funds and amounts charged to participants in the plan), and transaction fees (fees related to moving money, such as withdrawals or loans).
Why is 401(k) benchmarking important?
The process of 401(k) benchmarking is important for making sure a 401(k) plan is a quality plan and that it is in compliance with ERISA rules. An employer has a fiduciary duty to act in the best interest of their employees, and ensuring that a 401(k) plan has reasonable fees is part of that due diligence. Benchmarking can also help protect an employer and reduce their liability.
Photo credit: iStock/MicroStockHub
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
This article is not intended to be legal advice. Please consult an attorney for advice.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
SOIN-Q425-026
Read more