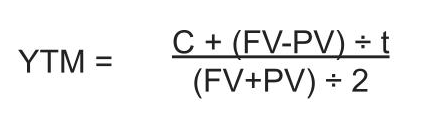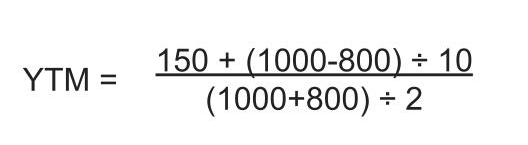15 Ways to Boost Your Curb Appeal for a Winter Open House
If you’re planning a winter open house, you might think there’s not much you can do to boost your curb appeal. In summer, you can clean up the lawn, add new plants, and set out an Adirondack chair in a cool color. But in the depths of winter, it may feel hopeless. However, there’s actually a lot you can do to boost your curb appeal for a winter open house.
Key Points
• Focus on the front door to create a great first impression for potential buyers.
• Use winter-friendly plants and take advantage of other landscaping techniques.
• Clean household hot spots such as the gutters to maintain a tidy appearance during winter.
• Use lighting strategically to welcome potential homebuyers who visit in winter’s dim late-afternoon hours.
• Consider minor repairs to capitalize on curb appeal.
How to Prepare for an Open House
No matter the season, there are some things that hold true: You always want your home to give off a great first impression. Whether it’s raining, snowing, or sunny, that means cleaning up the lawn, tidying the driveway, and doing other basic maintenance.
In winter, you may face some additional challenges. Let’s look at 15 things you can do that help with a winter open house, so you can sell your current abode, free up funds for your next home purchase, secure a mortgage loan, and get moving!
1. Start at the Front Door
No matter what the weather is doing, you can always spruce up your front door. There are still plenty of people buying a home in the winter, and you can give those folks a stunning first impression of your house. It will greet potential buyers before they ever step inside. A fresh welcome mat and a charming wreath or decorative array of pine cones can go a long way in this regard. You can also do some basic cleaning no matter what the season. Tidiness can give you more of an edge than you might imagine, and it’s a truly affordable way to improve your home — it doesn’t take a home equity line of credit to pay a local teenager to help you clean out the garage!
2. Find Plants that Work in Winter
You might think you can only refresh the garden in summer and spring, but there are several plants that thrive in colder weather, depending on where you live. Holly is a popular choice that adds color all winter. Another idea is to grab some pots of mums from your local supermarket or garden center to bring some greenery to the front door area on the day of your open house.
3. Don’t Forget the Birds
It isn’t just plants that are surprisingly hardy in winter. If you have birds in spring and summer, they may be around in winter, too. Hanging a bird feeder can entice them to flit about your yard, which will charm visitors. If you already have bird feeders for the warmer months, prepare for the open house by adding seeds.
Recommended: Mortgage Calculator with Taxes and Insurance
4. Know the Trends
You don’t have to go it alone when trying to figure out how to prepare for an open house. Look up the current housing market trends by city. This can show you not only what’s selling, but perhaps why it’s selling. See what other sellers are doing to improve their curb appeal. Take a look at the listings and let them inspire you.
5. Turn on the Lights
You can use outdoor lighting to not only make your home more attractive, but also safer. You don’t want prospective buyers stumbling through the late-afternoon dark or approaching nervously because they are unsure if the house is open. Add more lighting if you can. You can line a pathway with lights, for example, for both safety and aesthetics.
6. Check the Gutters
In winter, the gutters can take a beating. Make sure you clean out snow, leaves, and other debris that tends to build up during bad weather. Overstuffed gutters just aren’t a good look.
7. Clean the Walkways
A winter open house shouldn’t require snow shoes. Make sure the walkways to and from the house are clean and clear. Shoveling snow isn’t fun, but it will make a much better impression when buyers pull up in front of your house.
8. Don’t Hide Those String Lights
You might think that you have to prepare for an open house by hiding all the holiday lighting, but string lights can add a stylish touch to your home. Don’t go overboard like something out of “National Lampoon’s Christmas Vacation,” but do think about having some in the front of your house, whether around the front door or on some shrubs by the entryway.
9. Put on a Fresh Coat of Paint
There’s no wrong season for a fresh coat of paint. If you get the opportunity and have the budget, try painting your entry area — or your entire home if you’re in a warm part of the country. It can make your home look crisp and well cared for.
10. Paint Your Front Door a Bright Color
Don’t have the time or budget to repaint the whole house? Even just painting the front door can add a fresh splash of color that boosts your home’s curb appeal. Some colors to consider: bright red, like the color of an English double-decker bus, or sunny yellow. (Don’t forget to track your costs if you do more than routine maintenance, as they may help offset capital gains tax on the sale of your home.)
11. Make Sure the House Number Is Visible
When it comes to curb appeal, you also have to think about the literal curb. Is your house number visible from the street? If not, consider updating those numbers to make them visible and chic.
12. Spruce Up the Mailbox
While you’re looking at your house numbers, why not reconsider your mailbox as well? Perhaps you get a brand-new one, or give your current one a fresh coat of paint, so it pops.
13. Do a Quick Roof Fix-Up
Maybe you’ve lived with a few broken or missing roof shingles or tiles for so long, you hardly notice them. Sorry to say, prospective buyers may well zero in on them the second they walk up your front path. After all, a new roof is among the more costly repairs a buyer will encounter. It’s wise to get those repaired before you welcome your home shoppers.
Recommended: What Are the Most Common Home Repair Costs?
14. Refresh Your Landscaping
Applying a layer of mulch (after the first few hard frosts) can help protect plants from winter’s chill and make your landscaping look tidy and clean.
15. Use Fake Plants
You don’t have to be 100% authentic with your decorations. Topiaries shaped like trees or grapevine balls can make your porch more appealing. And they’ll likely stand up to any weather winter can throw at them. And when winter is over, simply store them away.
The Takeaway
You might feel discouraged at first when wondering how to maximize curb appeal for an open house in winter. But it’s a lot easier than it seems. There’s no point trying to fake spring or summer flowers, so opt for cleaning up, some greenery (real or artificial), some lighting, and perhaps a pop of color. Then sit back and wait for the buyers to come, so you can move on to a new home of your own.
Looking for an affordable option for a home mortgage loan? SoFi can help: We offer low down payments (as little as 3% - 5%*) with our competitive and flexible home mortgage loans. Plus, applying is extra convenient: It's online, with access to one-on-one help.
FAQ
What is the best day of the week to host an open house?
Saturday open houses often conflict with family activities, such as sports games, but Sunday may conflict with religious observation. Which of these is the lesser problem depends on the property you are selling, the community you live in, and the type of house you are selling. A real estate agent experienced in your local market will likely have the best advice on whether Saturday or Sunday is a better day for your specific property.
Is winter a bad time to sell a house?
Winter is traditionally considered a slow season for home sales, but if you are ready to put your home on the market, don’t let the time of year hold you back. You may find there is less competition from other properties, and that real estate agents have more time and attention for your property. If the market is less busy, you may also be able to close on the sale faster.
Photo credit: iStock/Korisbo
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
SoFi Mortgages
Terms, conditions, and state restrictions apply. Not all products are available in all states. See SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria for more information.
²SoFi Bank, N.A. NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC), offers loans directly or we may assist you in obtaining a loan from SpringEQ, a state licensed lender, NMLS #1464945.
All loan terms, fees, and rates may vary based upon your individual financial and personal circumstances and state.You should consider and discuss with your loan officer whether a Cash Out Refinance, Home Equity Loan or a Home Equity Line of Credit is appropriate. Please note that the SoFi member discount does not apply to Home Equity Loans or Lines of Credit not originated by SoFi Bank. Terms and conditions will apply. Before you apply, please note that not all products are offered in all states, and all loans are subject to eligibility restrictions and limitations, including requirements related to loan applicant’s credit, income, property, and a minimum loan amount. Lowest rates are reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Products, rates, benefits, terms, and conditions are subject to change without notice. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria. Information current as of 06/27/24.In the event SoFi serves as broker to Spring EQ for your loan, SoFi will be paid a fee.
*SoFi requires Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) for conforming home loans with a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio greater than 80%. As little as 3% down payments are for qualifying first-time homebuyers only. 5% minimum applies to other borrowers. Other loan types may require different fees or insurance (e.g., VA funding fee, FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums, etc.). Loan requirements may vary depending on your down payment amount, and minimum down payment varies by loan type.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
SOHL-Q424-116
Read more