Crypto Staking: A Beginner’s Guide to Earning Passive Income With Crypto
Table of Contents
Crypto staking is a way to use crypto holdings to generate rewards while helping to validate transactions. While “staking” may be a relatively new addition to the financial lexicon, it’s important for those interested in crypto to understand what it is, how it works, and what cryptocurrencies it can be used to obtain.
Crypto staking may feel like it’s a step beyond simply learning how to buy cryptocurrencies or how a crypto exchange works, but learning about cryptocurrency staking can broaden your knowledge of the crypto ecosystem, making you more informed about your options.
Key Points
• Crypto staking involves pledging crypto holdings to a blockchain network to earn rewards, while supporting transaction validation on the blockchain.
• Staking is more energy-efficient and accessible compared to mining.
• Popular staking coins include Ethereum, EOS, Tezos, and Polkadot.
• Staking yields can range from approximately 0.40% to 18% annually.[1]
• Crypto staking can be high risk given the high volatility of crypto assets and potential network security concerns.
What Is Crypto Staking?
Crypto staking is the process of “locking up” crypto holdings on a blockchain network in order to try and obtain rewards. There may be time limits or requirements depending on the specific blockchain network, and rewards can vary significantly, but are typically a percentage of the coins staked.
Cryptocurrencies are built with blockchain technology, in which crypto transactions are verified, and the resulting data is stored on the blockchain. Depending on the types of cryptocurrency you’re working with and its supporting technologies, these validation processes may involve staking, using a “proof-of-stake” consensus mechanism, or mining, using a “proof-of-work” consensus mechanism. Each of these processes help crypto networks achieve consensus, or confirmation that all of the transaction data adds up to what it should.
Crypto is
back at SoFi.
SoFi Crypto is the first and only national chartered bank where retail customers can buy, sell, and hold 25+ cryptocurrencies.
Staking vs Mining: What’s the Difference?
Staking crypto generates rewards and helps a crypto network validate information on the blockchain, using the cryptocurrency stakers locked up on the network. Crypto mining has the same goal, but the consensus needed to verify transactions is achieved in a different way.[2]
Effectively, mining involves using computing power to solve mathematical problems and equations to open up new blocks on a blockchain, for which miners are then rewarded. Mining requires significantly more computing power and resources, but effectively, both staking and mining are trying to achieve the same ends of validating information and producing new “blocks.”
The Role of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Achieving consensus and validating information on a blockchain requires participants. That’s what staking is: individuals who actively hold onto, or lock up their crypto holdings in their crypto wallet, may participate in these networks’ consensus-taking processes. Stakers are, in essence, approving and verifying transactions on the blockchain.
For doing so, the networks reward those individuals. The specific rewards will depend on the network.
It may be helpful to think of crypto staking as similar to depositing cash in a savings account. The depositor earns interest on their money while it’s in the bank, as a reward from the bank, who uses the money for other purposes (lending, etc.). Staking coins is, from that perspective, similar to earning interest. Although cryptocurrency holdings could potentially lose value as the market ebbs and flows, too.
How Does Crypto Staking Work?
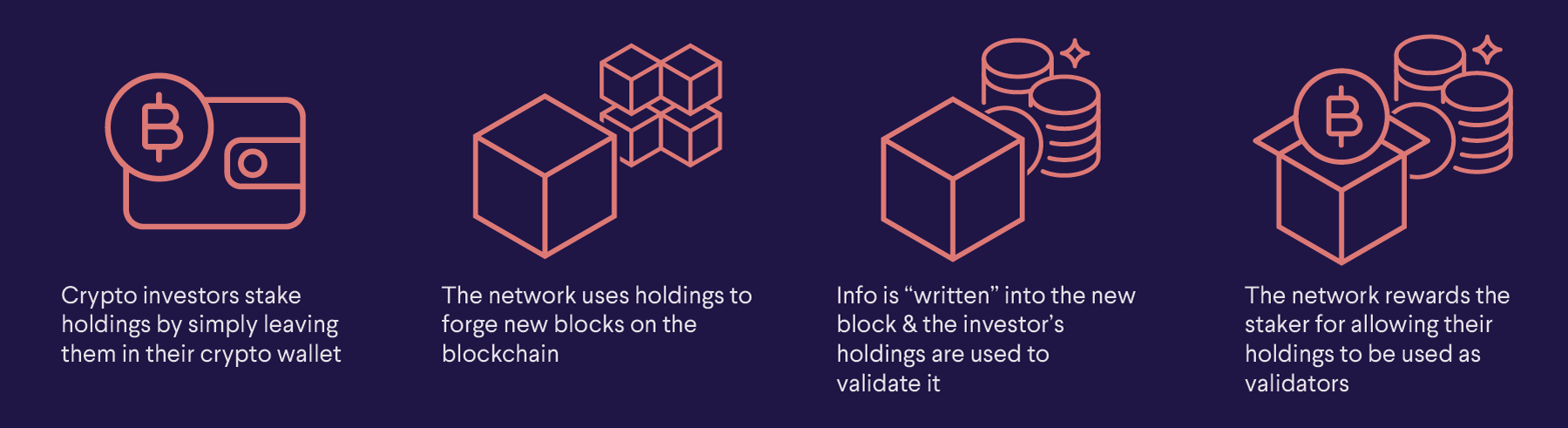
Crypto staking is typically a passive activity, unless you actively run a blockchain validator node. When someone stakes their holdings (typically by locking them in a wallet through a crypto staking platform), the network can use those holdings to forge new blocks on the blockchain.
The more crypto you’re staking, the better the odds are that your holdings will be selected to validate information and new blocks, and a lot of that depends on the specific blockchain network you’re staking on.
Essentially, during a transaction, information is “written” into the new block, and the staker’s holdings are used to validate it. Since coins already have “baked in” data from the blockchain, they can be used as validators. Then, for allowing those holdings to be used as validators, the network rewards the staker.
How to Start Crypto Staking
To start crypto staking, a person needs to decide where and what they want to stake. Here are four simple steps to get started.
1. Choosing a Proof-of-Stake Cryptocurrency
To begin staking cryptocurrency independently, a user would have to decide which coin they want to stake and buy their cryptocurrency of choice.
Ethereum (ETH), for example, requires a minimum of 32 ETH (worth about $123,000 at the time of writing) for users to begin staking.[3]
2. Choosing a Staking Platform
You may be able to stake crypto through an exchange network, through a staking service, or directly through the cryptocurrency itself.
3. Choosing Your Wallet and Hardware
Typically, after choosing a platform, you would then download a crypto wallet in which to store your coins for staking. That may mean going directly to the specific crypto’s main website and downloading its corresponding wallet.
To stake crypto, users need a constant, uninterrupted internet connection. A standard dedicated desktop computer will likely do the job, although a Raspberry Pi might save on electrical costs.
4. Begin Staking
Once the hardware has been selected and the crypto wallet software downloaded, a user can begin staking cryptocurrency.
For those holding the appropriate crypto in an exchange-hosted crypto wallet, the exchange typically handles all the staking on the backend.
Depending on the specific crypto, wallet, or exchange network, that may be all the action a person needs to take. But it’s a good idea to double-check to see if additional steps need to be taken.
What Are the Different Ways to Stake Crypto?
There are also a few different ways to stake crypto.
Staking on an Exchange
Perhaps one of the simplest ways to stake crypto is to do so through your given exchange. Many crypto exchanges give people the option to stake, and in those cases, depending on the exchange, they may simply need to select the option to stake, lock up their holdings, and let the rewards generate.
Delegated Staking and Staking Pools
Aside from an exchange, stakers may be able to delegate their crypto holdings to pools, which will allow them to generate rewards, too. This can’t be done for every cryptocurrency, but for those that do have delegated staking and pooling built into their networks, it can be a way to stake directly to a validator or delegate.
Running Your Own Validator Node
If you’re really feeling up for it and want to get more deeply involved on a specific blockchain network, you could look at running your own validator node, also referred to as solo staking. Note, however, that doing so likely requires some significant background knowledge, and there’s the potential of making mistakes. It could also require some hardware that could cost hundreds or thousands of dollars.
The Pros and Cons of Crypto Staking
There are some pros and cons to staking crypto.
| Crypto Staking Advantages | Crypto Staking Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low energy usage | Different security measures |
| Easier to earn rewards | Potential for takeover |
| No special hardware needed | Increased centralization |
The Benefits of Staking
Here are a few of the potential benefits of staking:
• Less energy-intensive. PoS networks use less energy than PoW platforms. Each mining machine requires a constant supply of electricity and consumes much more power than a regular computer. But it’s possible to run validator nodes on an average computer, eating up fewer resources, to power your staking activity
• Easier to earn rewards. Crypto staking and mining rewards can be very different. Almost anyone can stake a small amount of crypto on a crypto exchange and earn some kind of yield. To become a miner, however, often requires a much bigger commitment. First, you’d need to acquire the proper computer, which can be costly; then you’d need to learn to use it, which can be time-consuming.
• No special equipment required. Anyone can become a validator using a regular computer, assuming they have enough money and can keep the node running constantly. By contrast, mining requires specialized hardware.
The Risks of Staking
Conversely, there are some risks of staking that individuals should know about.
• Different security measures. PoS is relatively new compared to PoW. It’s not necessarily unsafe, but it’s also not inherently more secure than PoW, either. There are different security measures in place, and a lot of that depends on the specific network as well.
• Potential for takeover. Crypto blockchain networks may be controlled by those who hold the majority (or 51%) of tokens. While attacking a PoW network would involve acquiring large amounts of computing power, in many cases, attacking a PoS network could only require funding (again, depending on the specific network). Smaller blockchain networks are generally more vulnerable to a PoS “51% attack,” where attackers may try to manipulate transactions to their own advantage. However, PoS networks may also provide some inherent protection against these attacks. For example, attackers attempting such an attack risk losing the entire amount that’s staked.
• Increased centralization. The creator(s) of blockchain technology intended for blockchains to be decentralized. But in some cases, PoS networks can wind up becoming more centralized because becoming a validator can be more expensive than becoming a miner. Ethereum (ETH), for example, plans to change from PoW to PoS. To become an ETH validator would require 32 ETH (or around $123,000 as of summer 2025). Many centralized exchanges have chosen to become validators of PoS coins to share staking rewards with their customers.
How to Choose the Best Coins for Staking in 2025
Just a few years ago, the entire concept of proof-of-stake consensus was still relatively new, and options for staking coins were few and far between. But a growing number of projects are utilizing PoS and some exchanges are making it easier than ever for users to passively earn crypto by staking their coins.
With that in mind, the list of potential cryptos to stake, and the ones offering the highest potential yields, is always changing. But here are some of the cryptos out there that are viewed as more established.
• Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum (ETH) is one of the most popular cryptocurrencies on the market — although it is not exactly a cryptocurrency itself. Staking Ethereum on your own will require a minimum of 32 ETH. Rewards vary, too.
• EOS (EOS): EOS is similar to Ethereum in that it’s used to support decentralized blockchain systems and projects. EOS tokens are native to the EOS blockchain, and like other cryptos, can be staked to earn rewards.
• Tezos (XTZ): Like EOS and Ethereum, Tezos (XTZ) is an open-source blockchain network with its own native currency, with a symbol of XTZ. And it, too, can be staked on certain platforms and networks.
• Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot is a newer cryptocurrency, created in August 2020. Polkadot is both a cryptocurrency and a protocol designed to support “parachains,” which allow different blockchains created by different developers to share information securely.
• Avalanche (AVAX): Avalanche was created in 2020, and is one of the highest yield-producing cryptos out there for staking.
It’s important to research your options to understand whether staking a certain cryptocurrency would be right for you. Also be aware, as mentioned earlier, that SoFi does not currently offer staking services. While members will soon be able to buy, sell, and hold certain cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, other cryptocurrencies listed above may not be offered.
Factors to Consider
As with any financial transaction, it’s always important to consider the potential risks of crypto staking. As outlined, there are multiple risks to weigh, and when it comes to staking specifically, you’ll want to think about the potential staking rewards you could earn versus how your holdings could otherwise be used to generate returns.
There can be numerous things to take into account, but when it comes to staking, consider the reliability of a given crypto network, volatility, security, and opportunity costs.
Is Crypto Staking Worth It?
Anyone can earn crypto by staking cryptocurrency. But unless someone is sitting on a huge stash of proof-of-stake coins, they’re not likely to get rich from staking.
Staking rewards, as mentioned above, are in some ways similar to earning interest on funds held in a savings account. Both are a form of passive income (with the possible exception of solo staking). They don’t require a user to do anything other than holding the right assets in the right place for a given length of time. The longer a user stakes their coins, the greater potential for generating bigger rewards.
But unlike savings accounts, there are a few variables particular to proof-of-stake coins that influence how much of a staking reward users are likely to receive. Users would do well to research these factors and more when searching for the most profitable staking coins:
• Potential reward size
• The size of the staking pool
• The size of holdings locked, or required to stake
Additionally, the fiat currency value of the coin being staked must also be taken into account. Assuming this value remains steady or rises, staking could potentially be profitable. But if the price of the coin falls, profits could diminish quickly.
The Takeaway
Staking is a way to use your crypto holdings or coins to earn additional rewards. It can be helpful to think of it as along the lines of funds generating interest in a savings account over time.
Essentially, coin holders allow their crypto to be used as a part of the blockchain validation process, and are rewarded by the network for the use of their assets. While there are risks to be aware of, such as the value of the cryptocurrency itself falling, staking may open up another potential avenue for generating returns.
SoFi Crypto is back. SoFi members can now buy, sell, and hold cryptocurrencies on a platform with the safeguards of a bank. Access 25+ cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana, with the first national chartered bank to offer crypto trading. Now you can manage your banking, investing, borrowing, and crypto all in one place, giving you more control over your money.
FAQ
How much can you earn from crypto staking?
How much you could potentially earn from crypto staking depends on the specific crypto and given return rates associated with it. Rewards can range wildly.
Is staking crypto safe?
Staking crypto comes with risk, including the risk that the cryptocurrency loses value while it’s locked, but some staking set ups may be riskier than others. As always, do some research to try and get a sense of how risky staking a specific crypto could be, as there can be some significant risks associated with certain assets.
Can you lose money by staking crypto?
It is possible to lose money by staking crypto since holdings are locked up and values can change, or there may be penalties and vulnerabilities on a given platform or within a specific blockchain network.
What is the difference between crypto staking and lending?
Staking involves earning rewards (typically in the form of cryptocurrency) by locking up your crypto holdings with a blockchain network to help it validate transactions. Lending involves lending cryptocurrency holdings to a borrower in order to earn interest. Note that crypto lending can come with the risk of the borrower not returning the borrowed holdings.
Do you have to pay taxes on staking rewards?
Yes, rewards earned from crypto staking (or crypto mining) are taxed as ordinary income. Taxpayers are required to report the fair market value of the cryptocurrency rewards in U.S. dollars at the date and time those rewards are made available to them.
The same cryptocurrency holdings may also be subject to capital gains taxes when they’re sold, exchanged for another cryptocurrency, or disposed of in another way. Capital gains and losses from those transactions must be reported to the IRS.
About the author
Article Sources
- Bitcompare. Crypto Staking Rewards Comparison.
- Cornell Law School. consensus mechanism.
- Ethereum.org. Earn rewards while securing Ethereum.
Photo credit: iStock/FreshSplash
CRYPTOCURRENCY AND OTHER DIGITAL ASSETS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
Cryptocurrency and other digital assets are highly speculative, involve significant risk, and may result in the complete loss of value. Cryptocurrency and other digital assets are not deposits, are not insured by the FDIC or SIPC, are not bank guaranteed, and may lose value.
All cryptocurrency transactions, once submitted to the blockchain, are final and irreversible. SoFi is not responsible for any failure or delay in processing a transaction resulting from factors beyond its reasonable control, including blockchain network congestion, protocol or network operations, or incorrect address information. Availability of specific digital assets, features, and services is subject to change and may be limited by applicable law and regulation.
SoFi Crypto products and services are offered by SoFi Bank, N.A., a national bank regulated by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency. SoFi Bank does not provide investment, tax, or legal advice. Please refer to the SoFi Crypto account agreement for additional terms and conditions.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOCRYP-Q325-046
SIPS_3335350_001





