What Is Gamma in Options Trading?
Editor's Note: Options are not suitable for all investors. Options involve risks, including substantial risk of loss and the possibility an investor may lose the entire amount invested in a short period of time. Please see the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options.
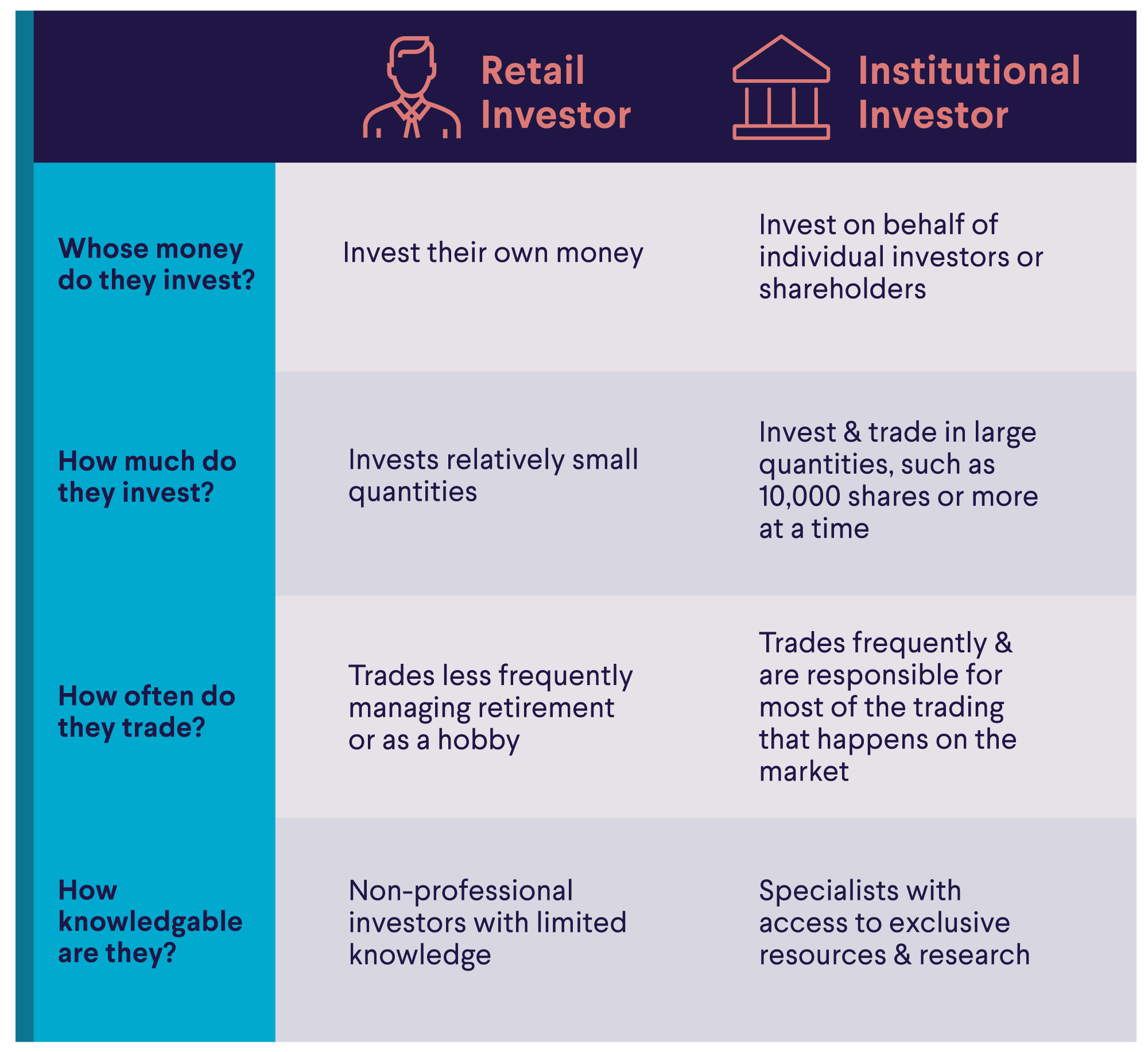
Gamma measures how much an option’s delta changes for every $1 price movement in the underlying security. You might think of delta as an option’s speed, and gamma as its acceleration rate.
Gamma expresses the rate of change of an option’s delta, based on a $1 price movement — or, one-point movement — of the option’s underlying security. Traders, analysts, portfolio managers, and other investment professionals use gamma — along with delta, theta, and vega — to quantify various factors in options markets.
Key Points
• Gamma measures the rate of change in an option’s delta for every $1 movement in the underlying security’s price.
• Delta provides insight into how much an option’s price might move relative to its underlying security.
• Understanding gamma is essential for risk management, as it allows traders to gauge the risk in their options holdings.
• Traders may balance positive and negative gamma in their portfolio to manage the risk of rapid price movements.
• High gamma may make long options more responsive to price movements, potentially amplifying gains, but increases risks for short options near expiration.
What Is Gamma?
Gamma is an important metric for pricing contracts in options trading. Gamma can show traders how much the delta — another metric — will change concurrent with price changes in an option’s underlying security.
An option’s delta measures its price sensitivity, and gamma provides insight into how that sensitivity may change as the underlying asset’s price shifts.
Expressed as a ratio: Gamma quantifies the rate of change in an option’s delta relative to changes in the underlying asset’s price. As an options contract approaches its expiration date, the gamma of an at-the-money option increases; but the gamma of an in-the-money or out-of-the-money option decreases.
Gamma is one of the Greeks of options trading, and can help traders gauge the rate of an option’s price movement relative to how close the underlying security’s price is to the option’s strike price. Put another way, when the price of the underlying asset is closest to the option’s strike price, then gamma is at its highest rate. The further out-of-the-money a security goes, the lower the gamma rate is — sometimes nearly to zero.
Recommended: What Is Options Trading? A Guide on How to Trade Options
Calculating Gamma
Calculating gamma precisely is complex, and it requires sophisticated spreadsheets or financial modeling tools. Analysts usually calculate gamma and the other Greeks in real-time, and publish the results to traders at brokerage firms. However, traders may approximate gamma using a simplified formula.
Gamma Formula
Here is an example of how to calculate the approximate value of gamma. This formula approximates gamma as the difference between two in delta values divided by the change in the underlying security’s price.
Gamma = (Change in Delta) / (Change in Underlying Security’s Price)
Or
Gamma = (D1 – D2) / (P1 – P2)
Where:
• D1 represents the initial delta value.
• D2 represents the final delta value after a price change.
• P1 represents the initial price of the underlying security.
• P2 represents the final price of the underlying security.
Example of Gamma
For example, suppose there is an options contract with a delta of 0.5 and a gamma of 0.1, or 10%. The underlying stock associated with the option is currently trading at $10 per share. If the stock increases to $11, the delta would increase to 0.6; and if the stock price decreases to $9, then the delta would decrease to 0.4.
In other words, for every $1 that the stock moves up or down, the delta changes by .1 (10%). If the delta is 0.5 and the stock price increases by $1, the option’s value would rise by $0.50. As the value of delta changes, analysts use the difference between two delta values to calculate the value of gamma.
How to Interpret Gamma
Gamma is a key risk-management tool. By figuring out the stability of delta, traders can use gamma to gauge the risk in trading options. Gamma can help investors discern what will happen to the value of delta as the underlying security’s price changes.
Based on gamma’s calculated value, investors can see the potential risk involved in their current options holdings; then decide how they want to invest in options contracts. If gamma is positive when the underlying security increases in value in a long call, then delta will become more positive. When the security decreases in value, then delta will become less positive.
In a long put, delta will decrease if the security decreases in value; and delta will increase if the security increases in value.
Traders use a delta hedge strategy to maintain a hedge over a wider security price range with a lower gamma.
💡 Quick Tip: When people talk about investment risk, they mean the risk of losing money. Some investments are higher risk, some are lower. Be sure to bear this in mind when investing online.
How Traders Use Gamma
Hedging strategies can help professional investors reduce the risk of an asset’s adverse price movements. Gamma can help traders discern which securities to purchase by revealing the options with the most potential to offset losses in their existing portfolio.
Gamma hedging helps traders manage the risk of rapid delta changes by offsetting gamma exposure in their portfolio. This is typically done by holding a combination of options with positive and negative gamma.
If any of the trader’s assets are at risk of making strong negative moves, investors could purchase other options to hedge against that risk, especially when close to options’ expiration dates.
In gamma hedging, investors generally purchase options that oppose the ones they already own in order to create a balanced portfolio. For example, if an investor already holds many call options, they might purchase some put options to hedge against the risk of price drops. Or, an investor might sell some call options at a strike price that’s different from that of their existing options.
Benefits and Risks of Using Gamma
Gamma plays a crucial role in managing options positions, influencing how delta changes in response to price movements. While it can enhance trading strategies, it may also introduce certain risks.
Benefits of Gamma
Gamma in options Greeks is popular among investors in long options. All long options, both calls and puts, have a positive gamma that is usually between 0 and 1, and all short options have a negative gamma between 0 and -1.
Higher gamma means the option is sensitive to movements in the underlying security’s price. For every $1 increase in the underlying asset’s price, a higher gamma suggests that delta will change more significantly, potentially amplifying gains or losses depending on the trade’s direction.
When delta is 0 at the contract’s expiration, gamma is also 0 because the option is worthless if the current market price is better than the option’s strike price. If delta is 1 or -1 then the strike price is better than the market price, so the option is valuable.
Risks of Gamma
While gamma can potentially benefit long options buyers, for short options sellers it can potentially pose risks. For short options, a high gamma near expiration increases the risk of substantial losses if the underlying asset’s price moves sharply, since delta changes rapidly and can result in significant margin requirements or losses.
Another risk of gamma for option sellers is expiration risk. The closer an option gets to its expiration date, the less probable it is that the underlying asset will reach a strike price that is very much in-the-money — or out-of-the-money for option sellers. This probability curve becomes narrower, as does the delta distribution. The more gamma increases, the more theta — the cost of owning an options contract over time — decreases. Theta is a Greek that shows an option’s predicted rate of decline in value over time, until its expiration date.
For options buyers, this can mean greater returns, but for options sellers it can mean greater losses. The closer the expiration date, the more gamma increases for at-the-money options; and the more gamma decreases for options that are in- or out-of-the-money.
How Does Volatility Affect Gamma?
When a security has low volatility, options that are at-the-money have a high gamma and in- or out-of-the-money options have a very low gamma. This is because the options with low volatility have a low time value; their time value increases significantly when the underlying stock price gets closer to the strike price.
If a security has high volatility, gamma is generally similar and stable for all options, because the time value of the options is high. If the options get closer to the strike price, their time value doesn’t change very much, so gamma is low and stable.
Using Gamma Along With Other Options Greeks
Gamma is a key metric in options trading, providing insight into how delta changes as the underlying asset’s price fluctuates. It is one of the five primary Greeks that traders use to manage risk and develop options strategies. Each Greek helps measure different aspects of an option’s behavior, offering a more comprehensive view of market exposure. The Greeks are:
• Gamma (Γ): Measures the rate of change in delta as the underlying security’s price moves. Higher gamma means delta shifts more quickly, increasing both potential gains and risks.
• Delta (Δ): Measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in the underlying asset’s price. Delta helps traders understand how much an option’s price might move relative to its underlying security.
• Theta (θ): Represents time decay, indicating how an option loses value as it nears expiration. A higher theta means the option’s value declines more rapidly over time.
• Vega (ν): Reflects the impact of implied volatility on an option’s price. Higher vega suggests that increased volatility leads to larger option price swings.
• Rho (ρ): Gauges an option’s sensitivity to interest rate changes. Rho is more relevant for long-dated options, as interest rate fluctuations can significantly impact their value.
Understanding gamma alongside the other Greeks allows traders to refine their strategies and manage risk more effectively in the options market.
The Takeaway
Gamma and the Greeks indicators are useful tools in options trading for understanding derivatives and creating options trading strategies. However, trading in derivatives, like options, is primarily for advanced or professional investors.
SoFi’s options trading platform offers qualified investors the flexibility to pursue income generation, manage risk, and use advanced trading strategies. Investors may buy put and call options or sell covered calls and cash-secured puts to speculate on the price movements of stocks, all through a simple, intuitive interface.
With SoFi Invest® online options trading, there are no contract fees and no commissions. Plus, SoFi offers educational support — including in-app coaching resources, real-time pricing, and other tools to help you make informed decisions, based on your tolerance for risk.
FAQ
What is a good gamma for options?
A “good” gamma depends on the trading strategy. High gamma is beneficial for short-term traders who want quick delta changes, as it makes options more responsive to price movements. Lower gamma is preferred for longer-term strategies or hedging, as it provides more stability and reduces the need for frequent adjustments.
Should gamma be high or low when trading options?
Whether gamma should be high or low depends on your strategy and risk tolerance. High gamma is ideal for short-term trades or when expecting significant price moves, as it amplifies delta changes and potential gains but also increases risk. Low gamma, common in deep in-the-money or far out-of-the-money options, provides more stability and slower delta changes, making it better suited for longer-term strategies or conservative approaches.
How do you trade options using gamma?
Trading options using gamma helps traders assess delta changes, identify opportunities, and manage risk. High gamma options, often at-the-money and near expiration, allow for rapid delta shifts, benefiting short-term trades. Gamma hedging helps balance exposure by offsetting positive and negative gamma, reducing volatility in a portfolio.
What is the best gamma ratio?
A “good” gamma depends on the trading strategy. High gamma is beneficial for short-term traders who want quick delta changes, as it makes options more responsive to price movements. Lower gamma is preferred for longer-term strategies or hedging, as it provides more stability and reduces the need for frequent adjustments.
What happens to gamma when volatility increases?
When volatility increases, gamma decreases for at-the-money options and stays relatively stable for in- and out-of-the-money options. Higher volatility smooths delta changes, making gamma less sensitive, while lower volatility increases gamma, leading to sharper delta shifts.
Photo credit: iStock/Prostock-Studio
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Options involve risks, including substantial risk of loss and the possibility an investor may lose the entire amount invested in a short period of time. Before an investor begins trading options they should familiarize themselves with the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options . Tax considerations with options transactions are unique, investors should consult with their tax advisor to understand the impact to their taxes.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
¹Probability of Member receiving $1,000 is a probability of 0.026%; If you don’t make a selection in 45 days, you’ll no longer qualify for the promo. Customer must fund their account with a minimum of $50.00 to qualify. Probability percentage is subject to decrease. See full terms and conditions.
SOIN-Q125-105
Read more