Can You Have a Joint Retirement Account?
No matter what stage of life you’re in, it’s likely that planning for retirement may be looming in the back of your mind. And that’s a good thing: According to the Center for Retirement Research, 39% of households are at risk for not having enough to maintain their living standards in retirement.
One way to start your retirement savings plan is to work shoulder-to-shoulder with your partner. You’ve no doubt heard of joint checking accounts, but what about joint retirement accounts – is there such a thing? Unfortunately, no. But while retirement plans like a 401(k) or IRA do not allow for multiple owners, there are ways couples can plan their retirement savings together.
Key Points
• Joint retirement accounts are not available, but couples can coordinate their retirement planning.
• Reviewing retirement goals together helps couples align their financial strategies for the future.
• Each spouse can name the other as a beneficiary on their individual retirement accounts to ensure shared access to funds.
• Couples can each have their own IRAs and contribute based on their joint taxable income.
• Spousal IRAs allow a non-working spouse to contribute to an IRA, provided the other spouse has earned income.
How Couples Can Plan Together for Retirement
Although there are no joint retirement account options, you can prepare for your golden years together by combining retirement forces. Here’s how.
Review Your Retirement Goals as a Couple
Talking openly and honestly about your finances is one of the keys to building a healthy financial plan. A good first step is to have a productive conversation about your plans and goals for retirement with your significant other. Do you plan on staying in the same home during your retirement years? Perhaps you want to travel internationally once per year or buy a camper and travel across the country.
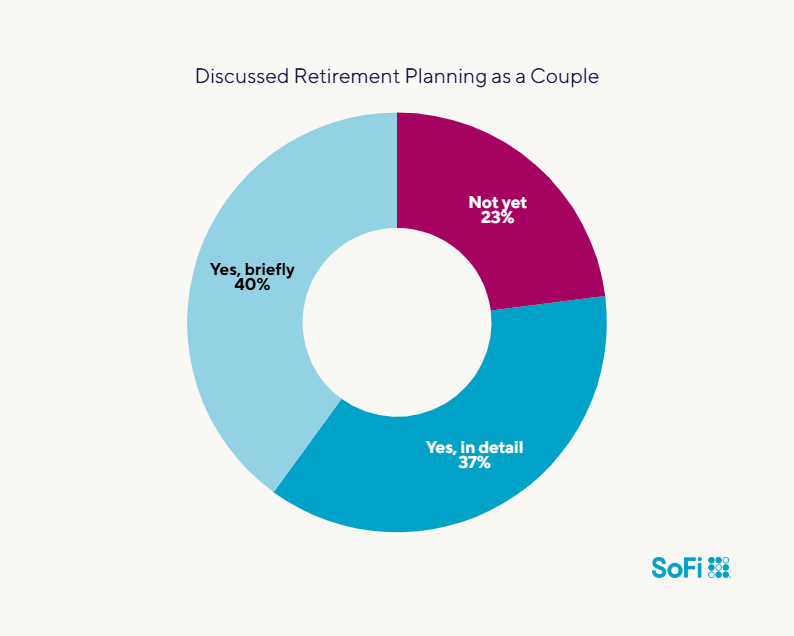
Many couples are talking about retirement early in their relationship. According to SoFi’s 2024 Love & Money Survey of 600 adults in the U.S. who have been married less than one year, 77% have discussed planning for retirement, including 37% who have talked about it in detail.
Source: SoFi’s 2024 Love & Money Survey
Determine the amount of money you want in retirement, too. While of course each couple’s retirement number is dependent upon their standard of living, you can calculate an estimate: Start with your current income, subtract estimated Social Security benefits, and divide by 0.04 to get your target number in today’s dollars.
Once you’ve put the numbers together and have a sense of how much you need to retire, you can figure out what you can safely withdraw to make your retirement last as long as you do.
💡 Quick Tip: Did you know that you must choose the investments in your IRA? Once you open an IRA and start saving, you get to decide which mutual funds, ETFs, or other investments you want — it’s totally up to you.
Determine When Both of You Will Retire
Do you know when you will retire? How about your partner? Remember, retirement plans like 401(k)s and IRAs generally cannot be withdrawn from penalty-free until you reach age 59 ½.
If you or your partner do plan to retire earlier than 59 ½, it might make sense to put some of your retirement funds into a taxable brokerage account that you can access at any time.
Name Your Spouse as a Beneficiary
While there are many ways to start saving for retirement, unfortunately, there aren’t any options that operate as a joint retirement account by default. A work-around to this is for each of you to name your spouse as a beneficiary in your retirement account. If something were to happen to one of you, the other person would still have access to your accounts and the money in it.
Your Top Questions About Joint Retirement, Answered
These are some of the biggest questions couples have when it comes to joint retirement.
Can both spouses contribute to a 401(k)?
No — only one spouse can contribute to a 401(k) account. 401(k)s are employer-sponsored plans. So just the spouse who works at the company offering the plan can participate in it and contribute to it.
However, the other spouse can be a beneficiary of the plan. This means that if the original planholder dies, the spouse gets the inherited 401(k) and can then roll it into their own 401(k) or into an IRA.
How much can a married couple contribute to a 401(k)?
As noted above, 401(k) plans are individual, with only one person contributing to each account (along with their employer, in some cases). The maximum annual 401(k) contribution allowed in 2025 is $23,500, with an additional catch-up contribution of $7,500 for those 50 and older — with a special “super catch-up” contribution limit of $11,250 for those aged 60 to 63 only. Those between age 60 and 63 could contribute $11,250 rather than $7,500, not in addition.
For 2026, the limits are $24,500 per year, and an additional $8,000 for those 50 and up — with the special “super catch-up” contribution limit of $11,250 for those aged 60 to 63 who could contribute $11,250 rather than $8,000.
With those figures in mind, in 2025 a married couple could each contribute $23,500 for a combined $47,000 per year, with the same catch-up provisions for those 50 and up, or 60 to 63. And in 2026, a married couple could each contribute $24,500 for a combined $49,000 per year, with the same catch-up contrbutions for those 50 and up, or 60 to 63.
How many IRAs can a married couple have?
If a couple is married and files their taxes jointly, each partner in the marriage can contribute to their own IRAs. There is a contribution limit, however — the total contributions to the IRAs “may not exceed your joint taxable income or the annual contribution limit on IRAs times two, whichever is less,” according to the IRS.
The annual IRA contribution limit is $7,000 for tax year 2025, so the total limit is $14,000 for the year. Those 50 and older can contribute an additional catch-up amount of $1,000 for 2025. The annual IRA contribution limit is $7,500 for tax year 2026, so the total limit is $15,000 for the year. Those 50 and older can contribute an additional catch-up amount of $1,100 for 2026. Note that the “super catch-up” amount does not apply to IRAs.
Recommended: How Many IRAs Can You Have?
Can my spouse contribute to an IRA if she doesn’t work?
Yes, a non-working spouse can open and contribute to an IRA (called a spousal IRA) as long as the other spouse is working and the couple files a joint federal income tax return. The spouse who doesn’t work can contribute up to the IRA limit of $7,000 in 2025 and $7,500 in 2026, plus $1,000 additional in catch-up contributions in 2025, and $1,100 in 2026, if they are 50 or older.
What is a spousal Roth IRA?
A spousal IRA is a Roth or traditional IRA for a spouse who doesn’t work. A couple must file their taxes as married filing jointly to be eligible for a spousal IRA. The spouse who doesn’t work can contribute up to the IRA limit of $7,000 in 2025, plus $1,000 additional in catch-up contributions if they are 50 or older. In 2026, the non-working spouse can contribute up to $7,500, plus an extra $1,100 in catch-up contributions if they are 50 or older.
Can a husband and wife both have a Roth IRA?
A husband and wife can each have their own separate Roth IRAs. Their total contributions to both IRAs must not exceed their joint taxable income, or the annual contribution limit to the IRAs, times two. For tax year 2025, each spouse can contribute $7,000 to separate Roth IRAs, making the total contribution limit $14,000 for those under age 50. Those 50 and up can each contribute an extra $1,000 if they choose. For tax year 2026, each spouse can contribute $7,500 to separate Roth IRAs, making the total contribution limit $15,000 for those under age 50. Those 50 and up can each contribute an extra $1,100 if they choose.
Can my non-working spouse have a Roth IRA?
Yes. Spousal IRAs can be traditional or Roth IRAs. In a Roth IRA, the money put into it is not tax deductible. Instead the money comes from taxable income but may grow tax free, so that an individual typically doesn’t have to pay taxes on the money that’s taken out of the account when they retire. While the contribution limits vary according to your tax filing and income status, typically the limit of contributions is the same as it is for traditional IRAs.
What is the maximum Roth contribution for a married couple?
In 2024, the annual limit for an IRA contribution is 7,000 per person, or $8,000 for those 50 and older. However, a Roth IRA has income limits. In 2024, a couple that is married filing jointly cannot contribute to a Roth IRA if their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is more than $240,000. Those with a MAGI between $230,000 and $240,000 can contribute a partial amount, and those whose income is less than $230,000 can contribute the full amount.
Should a married couple have two Roth IRAs?
Whether you should have two Roth IRAs is a personal decision. One consideration: Since a married couple cannot have a joint retirement account like a joint Roth IRA, if you each have a Roth IRA, you may be able to save more for retirement if you both contribute the full amount allowed to your separate IRAs. For 2024, that amount is $7,000 for those under age 50, and $8,000 for those 50 and up. However, your total contributions to both IRAs must not exceed your joint taxable income
The Takeaway
While no specific retirement savings plans — such as 401(k)s or IRAs — offer joint retirement accounts, there are ways for couples to plan and save for retirement together. One way is to each have your own separate IRAs that you contribute to. Another easy way to make sure you’re both taken care of in retirement is to make each other the beneficiaries on your individual accounts.
Prepare for your retirement with an individual retirement account (IRA). It’s easy to get started when you open a traditional or Roth IRA with SoFi. Whether you prefer a hands-on self-directed IRA through SoFi Securities or an automated robo IRA with SoFi Wealth, you can build a portfolio to help support your long-term goals while gaining access to tax-advantaged savings strategies.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Investment Risk: Diversification can help reduce some investment risk. It cannot guarantee profit, or fully protect in a down market.
SOIN0124060
CN-Q425-3236452-17




