How Do Student Loans Affect Your Credit Score?
Student loans don’t just help you pay for your college education. They also allow you to build a credit history, which can be useful when it comes time to get a mortgage or take out a car loan. The key, though, is to make regular on-time payment – or you may wind up with the sort of credit history that negatively impacts your ability to borrow money in the future.
Here’s a look at how student loans can affect your credit score.
How Is My Credit Score Calculated?
First, it can be helpful to know how your credit score is calculated. There are several types of credit scores, but FICO scores are the most commonly used by top lenders.
Your FICO score is calculated using five categories of data found in your credit reports, which each category weighted differently.
| Category | Weight in Scoring |
|---|---|
| Payment History | 35% |
| Amounts Owed | 30% |
| Length of Credit History | 15% |
| New Credit | 10% |
| Credit Mix | 10% |
Based on these calculations, there are a few ways you can build good credit and maintain a good credit score. Paying your bills on time is a big one, since your payment history is the most heavily weighted factor. Paying down existing debt and keeping credit card balances low will also have a big effect. Less impactful, but important strategies, also include diversifying the types of credit you have, avoiding opening too many new accounts at once, and keeping accounts open to lengthen the average age of your credit history.
Serious savings. Save thousands of dollars
thanks to flexible terms and low fixed or variable rates.
What Student Loan Factors Affect My Credit Score?
Now that you know how credit scores generally work, you might be wondering how your student loans specifically impact your score.
Again, one of the biggest ways your student loans can affect your credit is whether or not you pay them on time. If you’re a responsible borrower who continually makes on-time student loan payments, you will see positive shifts in your credit score over time.
But if you fail to repay a loan or continually make late payments, your credit score will likely see a dip. If you default on your student loan, your credit score could drop significantly. The lender may also send your account to a collections agency, and you may have a more difficult time securing credit in the future.
💡 Quick Tip: Get flexible terms and competitive rates when you refinance your student loan with SoFi.
How Does a Late Student Loan Payment Affect My Credit Score?
Making payments on time is important, but what you might not realize is exactly how damaging late payments can be. Even if your credit history is pristine, it only takes one report of 30 days past due to change your score. Once a late payment is reported to the credit bureaus, it could remain on your credit report for up to seven years.
To help ensure your payments are on time, you might want to set up an automatic payment plan. Most lenders will even give you a small discount on your interest rate for doing so. If you know you can’t make a payment on time, talk to your lender or loan servicer right away. The Department of Education, which is the lender for four types of Direct Loans, and even some private lenders, offer loan deferment or forbearance. These options allow a borrower to temporarily suspend payments, which will minimize the impact on their credit score.
Does It Hurt to Pay Off Student Loans Quickly?
Repaying student loans quickly will always improve your credit score, right? Not necessarily. In fact, you could even see a small, temporary dip in your credit score right after paying off a loan. There are several reasons for this. If student loans are your primary source of open credit, closing those accounts means you’re no longer building payment history. Prematurely paying off a loan can also change your credit mix or credit utilization.
But credit score is just one factor to consider when deciding how quickly to pay off a student loan. You may want to think about how much extra interest you’d pay by leaving the account open. Carrying a high loan balance could also make it harder to qualify for new loans, which is something to keep in mind when it comes time to buy a home or car.
Notorious Big Bad D’s: Delinquent and in Default
Student loans affect credit scores in a variety of ways, but the worst thing you can do is ignore your monthly loan payment. If you’re even one day late with a payment, you’ll be considered delinquent and may be charged a penalty.
Once a missed payment is more than 90 days delinquent, your loan servicer will report it to the three major national credit bureaus. This could lower your credit score and hurt your ability to get a new credit card or qualify for a car loan or mortgage.
After 270 days of a missed student loan payment, your status changes to default and your student loans are due in full along with any accrued interest, fines, and penalties.
(Note that the on-ramp that’s in place for federal student loan repayment from October 2024 through September 2025 temporarily shields borrowers from the most immediate consequences of delinquency and default.)
Will Rate Shopping Different Student Loan Lenders Hurt My Credit?
When you’re shopping around for the best interest rate possible on a private student loan, lenders may pull your credit file. This is called a hard inquiry, and each one could temporarily knock a few points off your credit score.
To help protect your FICO score, try to finish shopping for rates and finalizing your loan within 30 days. Researching rates and getting quotes ahead of time can give you a good idea of whether you’ll qualify for a loan before you formally apply.
You may also want to ask lenders if they can tell you the interest rate you would receive without doing a “hard” credit pull, which might affect your score. You can’t get a loan without an eventual hard inquiry, but getting prequalified allows you to compare interest rates without impacting your credit score.
Will Refinancing Student Loans Help My Credit?
Because refinancing involves taking out a new loan with new terms to pay off existing debt, refinancing student loans affects your credit score—both positively and negatively.
In the short-term, refinancing will involve a hard credit inquiry and may cause a temporary ding to your credit. Again, as long as you keep your loan shopping to a short period, multiple inquiries will be treated as one, and should have a minimal impact on your score.
In the long-run, refinancing student loans at a lower interest rate can have an indirect positive effect on your credit. For example, if refinancing lowers the amount you pay each month, you may be more likely to make payments on time. You may also pay off your loans faster, which can help you reduce your overall debt and improve your score. (Note: You may pay more interest over the life of the loan if you refinance with an extended term.)
If you refinance federal loans with a private lender — in effect, turning your federal loans into a private loan — rest assured that credit bureaus don’t view these two types of loans any differently. However, when you refinance your federal loans, you will lose certain federal protections, such as income-driven repayment plans, deferment or forbearance, and loan forgiveness programs.
Do I Need a Good Credit Score to Take Out a Student Loan?
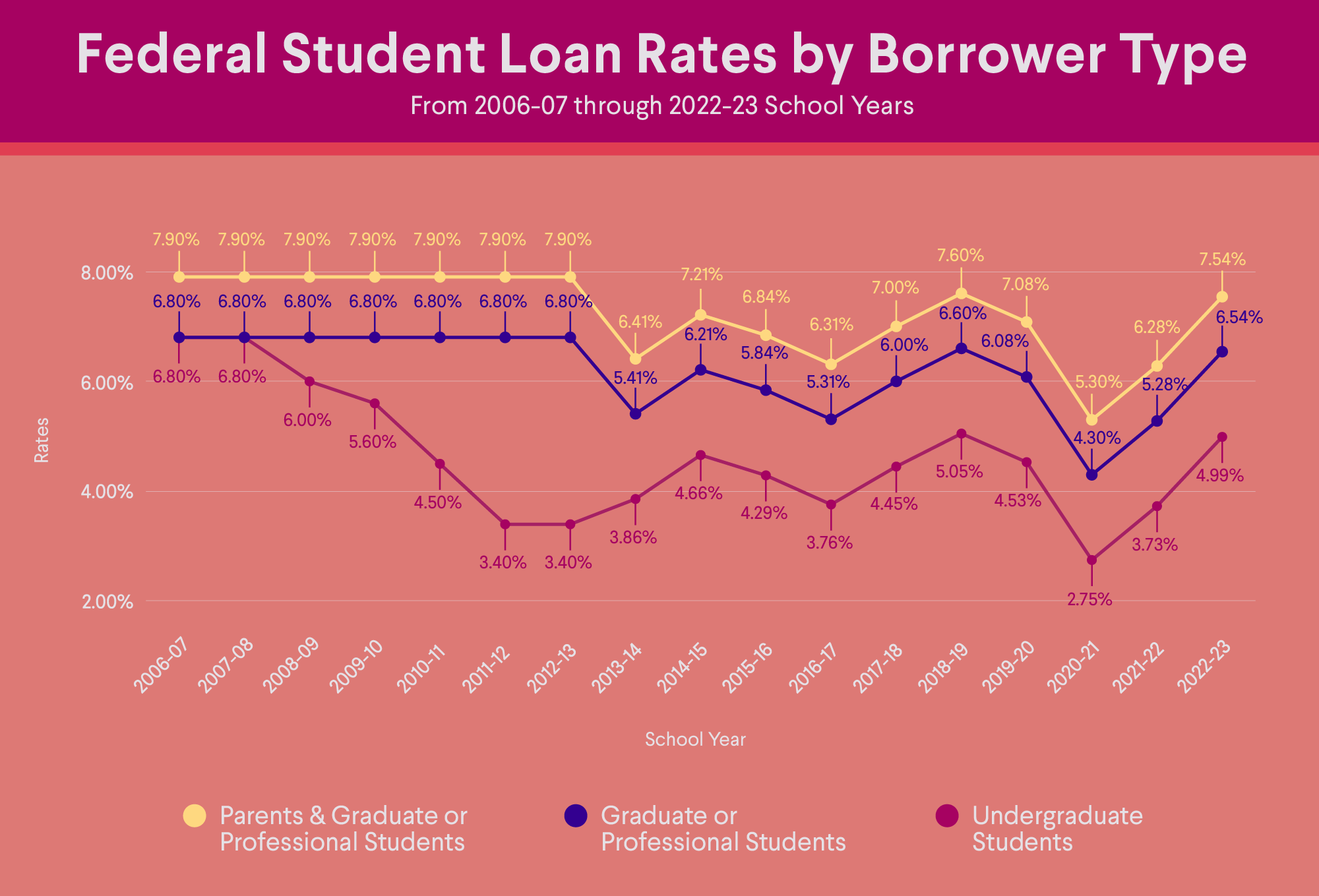
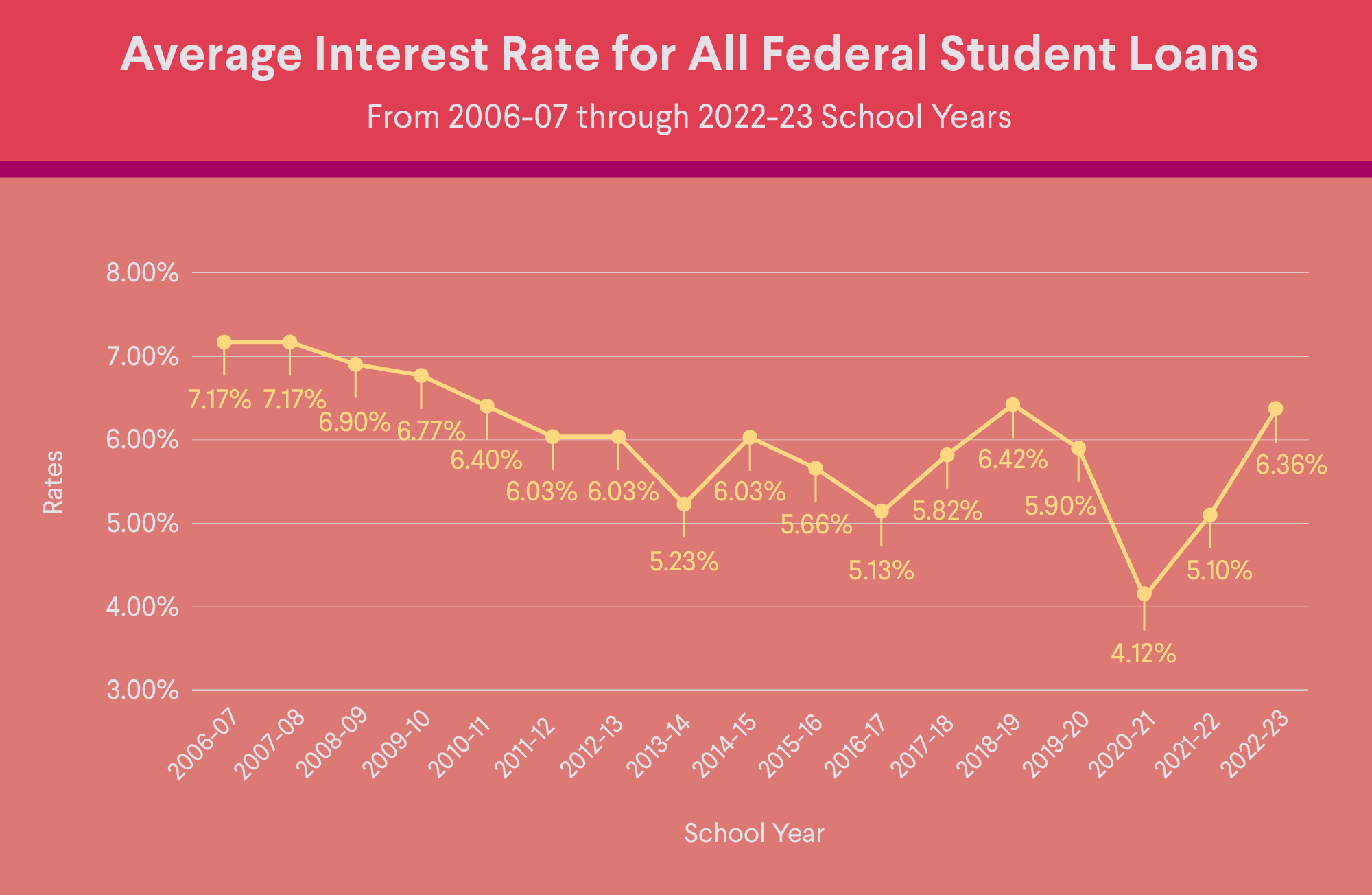
Your credit score may be a factor when you’re applying for a student loan. It all depends on the type of loan you’re planning to take out. Most federal loans don’t have a minimum credit requirement, which is why nearly every borrower gets the same interest rate regardless of their financial profile. However, federal PLUS loans for parents require that borrowers do not have an adverse credit history.
Credit scores are typically more of a factor with private student loans. Lenders often consider your score when determining student loan approval and interest rate. In general, the better your score, the better your rate will be.
💡 Quick Tip: Refinancing could be a great choice for working graduates who have higher-interest graduate PLUS loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and/or private loans.
Which Credit Scores Do Private Lenders Use?
When considering your student loan application, most private lenders look at your FICO® score. This score, which ranges from 300 to 850, helps lenders determine whether to extend credit and at what interest rate.
Because FICO is used widely throughout the lending industry, including by mortgage lenders and credit card providers, it gives lenders an apples-to-apples comparison of potential borrowers.
The Takeaway
Student loans can help borrowers establish a solid credit history, which can ease the way for future borrowing opportunities and attractive interest rates. The key is to pay what you owe on time, every time.
Paying a loan off early or shopping around for rates could cause a small, temporary dip in credit scores. Being late with a payment — or stopping payment altogether — may lower your credit score and hurt your ability to qualify for another loan.
Looking to lower your monthly student loan payment? Refinancing may be one way to do it — by extending your loan term, getting a lower interest rate than what you currently have, or both. (Please note that refinancing federal loans makes them ineligible for federal forgiveness and protections. Also, lengthening your loan term may mean paying more in interest over the life of the loan.) SoFi student loan refinancing offers flexible terms that fit your budget.
FAQ
Do student loans help build credit?
Student loans are an opportunity for borrowers to build credit and establish a solid credit history, which can help when it’s time to get a mortgage or take out a car loan. The key is to make regular, on-time payments.
How can I improve my credit score if I have student loans?
Payment history is one factor of your overall credit score, so making regular, on-time payments on your student loans can help you build credit.
How is my credit score determined?
Your credit score is calculated using five different categories of data. These include payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix.
About the author
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
SoFi Student Loan Refinance
Terms and conditions apply. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are private loans. When you refinance federal loans with a SoFi loan, YOU FORFEIT YOUR ELIGIBILITY FOR ALL FEDERAL LOAN BENEFITS, including all flexible federal repayment and forgiveness options that are or may become available to federal student loan borrowers including, but not limited to: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Income-Based Repayment, Income-Contingent Repayment, extended repayment plans, PAYE or SAVE. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
SoFi Private Student Loans
Please borrow responsibly. SoFi Private Student loans are not a substitute for federal loans, grants, and work-study programs. We encourage you to evaluate all your federal student aid options before you consider any private loans, including ours. Read our FAQs.
Terms and conditions apply. SOFI RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MODIFY OR DISCONTINUE PRODUCTS AND BENEFITS AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. SoFi Private Student loans are subject to program terms and restrictions, such as completion of a loan application and self-certification form, verification of application information, the student's at least half-time enrollment in a degree program at a SoFi-participating school, and, if applicable, a co-signer. In addition, borrowers must be U.S. citizens or other eligible status, be residing in the U.S., Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, or American Samoa, and must meet SoFi’s underwriting requirements, including verification of sufficient income to support your ability to repay. Minimum loan amount is $1,000. See SoFi.com/eligibility for more information. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. SoFi reserves the right to modify eligibility criteria at any time. This information is subject to change. This information is current as of 4/22/2025 and is subject to change. SoFi Private Student loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
Disclaimer: Many factors affect your credit scores and the interest rates you may receive. SoFi is not a Credit Repair Organization as defined under federal or state law, including the Credit Repair Organizations Act. SoFi does not provide “credit repair” services or advice or assistance regarding “rebuilding” or “improving” your credit record, credit history, or credit rating. For details, see the FTC’s website .
Non affiliation: SoFi isn’t affiliated with any of the companies highlighted in this article.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOSL0923044
Read more