Why College May Not Be for Everyone
While college is a good option for many people, it isn’t for everyone — and not going to a four-year college doesn’t mean you can’t have a meaningful career.
More people than ever before have a college degree, but a four-year program isn’t the only way to be successful. Even employers are realizing that there are many skills that can’t be captured in a degree program. In fact, some major tech companies, including Google and Apple, no longer require applicants to have a four-year degree for some of their positions.
There are certain jobs for which you need a college degree, like an electrical engineer, marketing manager, or teacher, but there are plenty of careers out there that don’t require additional degrees.
Keep reading for more on the pros and cons of going to college, alternatives to a college degree, and more.
Table of Contents
Key Points
• College may not suit everyone, and skipping it doesn’t preclude a successful career.
• Major tech companies are increasingly open to hiring individuals without a four-year degree.
• Specific careers require a college degree, but many do not.
• Alternatives like trade schools, apprenticeships, and certificate programs offer viable career paths.
• Taking a gap year or starting a business are potential options for those opting out of college.
Reasons Not to Go to College
There are a number of valid reasons to delay college — or put it off entirely. Here are some to consider:
• You’re not excited about your options. Maybe you didn’t get into the schools you expected to or you’re having second thoughts when you try to imagine yourself attending the schools you did get into. If the thought of college fills you with dread or doubt rather than excitement, taking a year off to reassess your options can be a good strategy.
• You’re unsure what career you are interested in pursuing. You may want to explore different options by being exposed to college-level courses at a community college, or spend time volunteering, working, or traveling.
• You’re already working. If you already have a job, you may be wanting to lean into your current job or save money to go to school in a few years.
• You’re exploring non-degree avenues. There are many high-paying trades that don’t require a degree, but may require on-the-job experience or an apprenticeship.
• You have a plan for a gap year. Some people like to take a year to travel, work, or otherwise take a break in between high school and college to further explore their identity and what they want to do in the future.
• You feel you’re going to college only to please your family. If you feel pressured to go to college, it may be a sign that college isn’t the right option for you, at least right now.
• You have essential family obligations. Some students need to help their families and may not be able to take time off to go to school. These students may consider community college or a part-time degree program. Speaking with your current high school counselor may help you find ways to juggle multiple responsibilities.
• You want to take time to pursue a talent. From sports to the performing arts to a creative path, some people choose to explore a talent more seriously, focusing time, energy, and resources prior to going to college. This can be a decision you make with the help of your family and any coaches or teachers.
Refi now to pay off loans &
reach your goals faster with a shorter term.
Reasons to Go to College
College can be a great time to grow and learn and, for some, it’s a natural step. Here are some other reasons why college may make sense:
• You’re excited and realistic about college. You recognize college may have ups and downs, but feel confident that college feels “right” as your next step — not just something your family or teachers expect from you.
• A college degree will help you achieve your career goals. You’ve done your research and/or talked with alums and people working in your targeted field and feel confident that college makes sense for your career goals.
• College fits into your overall financial plan. You have a sense of how much college will cost and a plan for how you will pay for it, which might include a combination of financial aid, savings, and federal or private student loans. You also want to make sure you will be able to manage any student loan payments after you graduate.
• You have a ‘Plan B’ in case you realize that college isn’t the right fit. Sometimes people realize one semester into school that college may not be what they need at that moment in their lives. It can be helpful to talk about what this may be, so that you don’t feel trapped if school doesn’t feel like it’s a good fit.
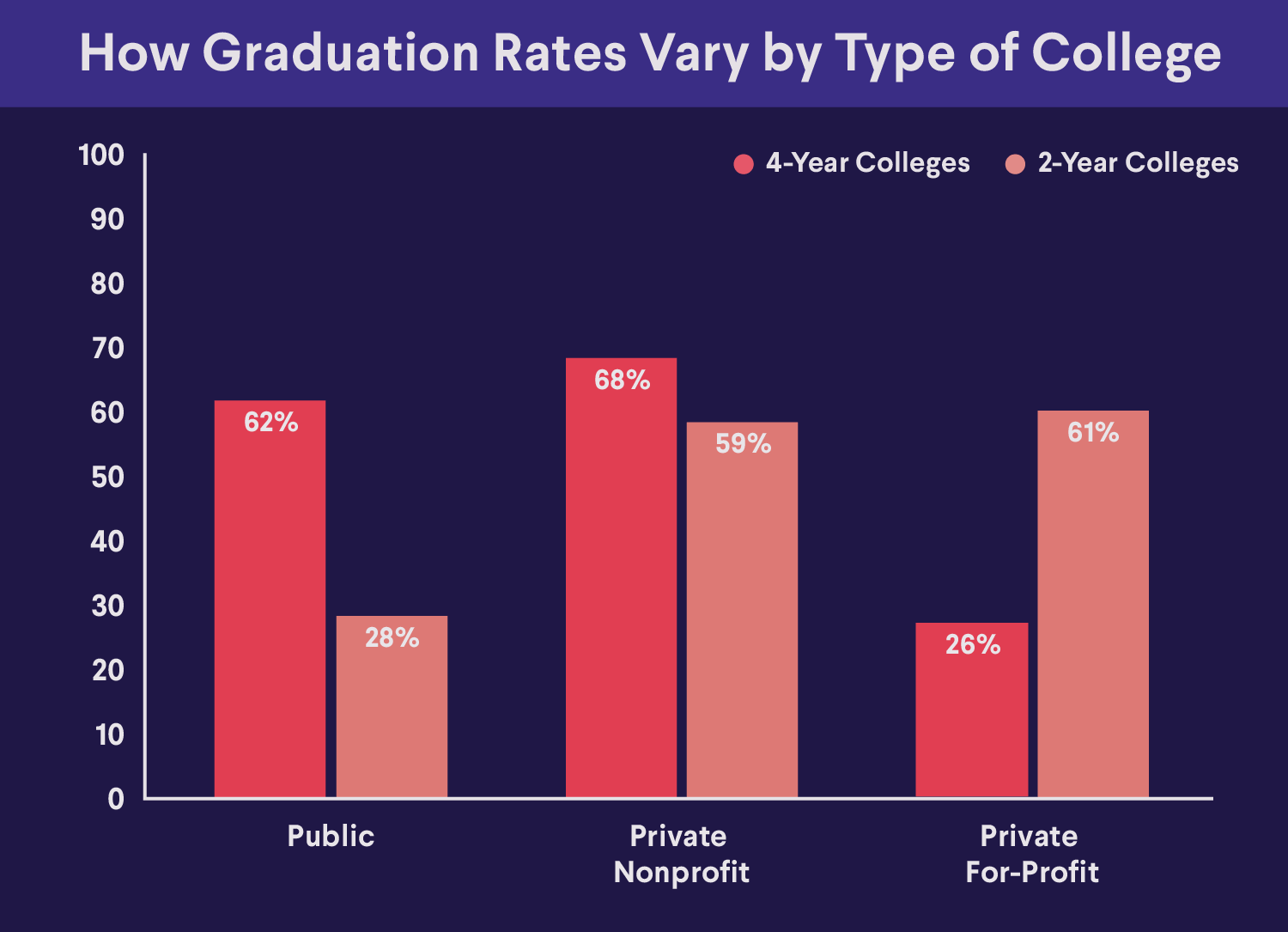
Source: National Center for Education Statistics
Recommended: Full-time vs Part-time Student
Alternatives to a College Degree
Just because you aren’t interested in a four-year degree doesn’t mean you need to forgo higher education entirely. Alternative educational models, like trade schools and community colleges, offer many practical certification and two-year associate degree programs that can help you get ahead.
It is important to know that even if you’re not planning to pursue a four-year degree, you still have options when it comes to creating a career that is right for you.
💡 Quick Tip: You’ll make no payments on some private student loans for six months after graduation.
Trade School
Sometimes known as technical or vocational schools, trade schools can prepare you for a specific job, such as a dental hygienist, electrician, cosmetologist, or web developer. These programs are normally much shorter than four years, and certain programs may allow you to finish in only a few months. There are both public and private trade schools.
Trade schools don’t award bachelor’s degrees. Instead, when you graduate from a trade school, you typically receive a diploma or certificate indicating that you are trained and certified to perform a specific job. Some trade school programs do offer associate degrees, which are the same type of degrees offered by many community colleges.
Community College
As mentioned above, community colleges usually offer two-year degrees called associate degrees. These degrees can either stand alone or be a stepping stone to obtaining a bachelor’s degree at a four-year school.
Many community colleges also offer career preparation programs that are designed to help students jump into the workforce without the need for a bachelor’s degree.
Community college could also be a great way to test out college life and see if you want to continue pursuing higher education. They tend to be much less expensive than four-year universities, which means it won’t cost you an arm and a leg before you decide if higher education is right for you.
Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships are paid positions designed to teach the apprentice about a specific job or industry. They can help you learn how to use industry-specific tools and technologies and help you develop your skills over a period of time. This may be in fields as diverse as plumbing to transportation engineering to baking.
Apprenticeships can be a win-win for employers and employees because they allow those starting out to begin working (and earning a paycheck) immediately, and they help employers fill vacant jobs.
Certificate Programs
Similar and sometimes overlapping with trade schools, certificate programs offer specialized training in a specific area. This may include coding, cybersecurity, yoga, fitness, getting a commercial driver’s license (CDL), or other areas where specialized knowledge may be a prerequisite. These certificates may also be helpful in making job seekers eligible for positions with higher starting salaries.
Recommended: Are Coding Bootcamps Worth the Money?
Taking a Gap Year
A gap year is when a student takes a year off between high school and college. Some colleges allow accepted students to defer for a year, holding a place for them in the next year’s incoming class. Some people create a travel itinerary; others may work or volunteer for the year. There are some gap year programs that create opportunities for students, but keep in mind that some programs may be costly.
Starting a Business
If you are already passionate about — and have a lot of knowledge about — a specific field or industry, you might consider skipping college altogether and jumping into that business.
Starting your own business takes a lot of hard work, but it could mean that you get to be your own boss and work in an industry you love. And because you could quickly become an expert on the products or services you provide, you aren’t necessarily at a disadvantage because you lack a degree.
Recommended: 9 High Paying Jobs That Don’t Require a Degree
If You Do Go the College Route
There are plenty of options if you choose not to attend a four-year college. However, there are also options within the world of college, including the type of college you choose, the major you decide to pursue, and how you pay for college.
There’s no denying that college can be expensive. In the 2024-25 school year, the average cost for tuition and fees at an in-state college was $11,610, while the average sticker price for a private college was $43,350. And, these numbers don’t include room and board. This can be a big financial commitment, especially if you are on the fence about pursuing higher education.
That’s why it can be a good idea to begin creating a payment strategy early. A great first step is to fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA®) to see how much federal aid — including scholarships, grants, work-study, and federal student loans — you qualify for.
Federal student loans do have limits on how much a student can borrow each year they are enrolled in school. Some students may need additional funds to bridge the gap. In that case, some may consider borrowing a student loan from a private lender to help cover college costs.
In general, it can be a smart idea to tap all your federal loan and grant options before you consider private student loans. That’s because federal loans offer some protections, such as deferment options, that private loans may not. However, private loans can cover up to 100% of the cost of attendance, including money to pay for books, room and board, and personal expenses.
💡 Quick Tip: Parents and sponsors with strong credit and income may find much lower rates on no-fee private parent student loans than federal Parent PLUS Loans. Federal PLUS loans also come with an origination fee.
The Takeaway
College can lead students on a new career path, but depending on your goals and other factors, may not be necessary. Some students may choose to pursue a trade or vocational program instead of a four-year degree, while others may simply want to wait a year or so to earn and save more money to cover the cost of going to college.
If you do decide to go to college, you’ll have to figure out a way to pay for it. Most students rely on a combination of cash savings, scholarships, grants, federal student loans, and private student loans.
If you’ve exhausted all federal student aid options, no-fee private student loans from SoFi can help you pay for school. The online application process is easy, and you can see rates and terms in just minutes. Repayment plans are flexible, so you can find an option that works for your financial plan and budget.
FAQ
Why do some people not like college?
Some people dislike college due to high costs, irrelevant coursework, lack of practical skills, social pressures, and the rigid structure that doesn’t suit everyone’s learning style.
What are some alternatives to college?
Alternatives to college include trade schools, apprenticeships, online courses, bootcamps, and self-directed learning. These options often offer practical skills, lower costs, and more flexible schedules.
What are the pros of not attending college?
Pros of not attending college include saving money, allowing for early career entry, providing hands-on experience, and offering more flexibility for personal or family responsibilities.
SoFi Private Student Loans
Terms and conditions apply. SOFI RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MODIFY OR DISCONTINUE PRODUCTS AND BENEFITS AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. SoFi Private Student loans are subject to program terms and restrictions, such as completion of a loan application and self-certification form, verification of application information, the student's at least half-time enrollment in a degree program at a SoFi-participating school, and, if applicable, a co-signer. In addition, borrowers must be U.S. citizens or other eligible status, be residing in the U.S., Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, or American Samoa, and must meet SoFi’s underwriting requirements, including verification of sufficient income to support your ability to repay. Minimum loan amount is $1,000. See SoFi.com/eligibility for more information. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. SoFi reserves the right to modify eligibility criteria at any time. This information is subject to change. This information is current as of 4/22/2025 and is subject to change. SoFi Private Student loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
Please borrow responsibly. SoFi Private Student loans are not a substitute for federal loans, grants, and work-study programs. We encourage you to evaluate all your federal student aid options before you consider any private loans, including ours. Read our FAQs.
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOISL-Q325-009
Read more



