Routing vs Account Number: What’s the Difference?
If you’re looking for your bank routing and account numbers, they are likely easier to find than you may think: You can locate them on your checks or by logging into your financial institution’s app, for instance.
That said, you probably don’t want to broadcast these digits to too many people. Your routing and account numbers are the keys to your banking kingdom.
Your account’s routing number designates which financial institution holds your money, while your account number identifies your own unique checking or savings account. As you go about your financial business, you will require these numbers for many transactions, from enrolling in direct deposit at your workplace to signing up for online bill pay.
Key Points
• A routing number is a nine-digit code that identifies a bank or credit union.
• An account number is a unique identifier for your specific bank account.
• Routing numbers are used for various financial transactions like direct deposit, bill pay, and wire transfers.
• Account numbers are private and should be kept secure to prevent fraud.
• You can find your routing and account numbers on checks, through online banking, in-app, or by contacting your bank.
What Is a Routing Number?
A routing number is a sequence of nine digits that identifies a bank or credit union, and each banking institution has a unique number. Here are some facts about routing numbers and how they work:
• A routing number is also sometimes referred to as an ABA number, in reference to the American Bankers Association, which assigns them. Routing numbers are only issued to federal or state-chartered financial institutions that are eligible to maintain an account at a Federal Reserve Bank.
• Your bank’s routing number and ACH routing number may or may not be the same digits. Check with your bank to be sure.
• The routing number required for making a wire transfer often differs from the routing number that is printed on your checks. That number can be found online or by contacting your bank.
• A small bank may only have one routing number, while a larger financial institution may have several (they typically vary by state). An online bank, which operates without physical branches, will typically have one routing number.
Purpose of a Routing Number in Banking
The purpose of a routing number is to identify the financial institution that is responsible for the payment and ensure that funds are sent to the right place in a financial transaction.
Routing numbers are generally required when reordering checks, paying bills, setting up direct deposit, or making tax payments. Making sure you have the right digits will help ensure smooth transactions.
What Is an Account Number?
While the routing number identifies the financial institution where your account is held, the bank account number represents your specific account. While anyone can find your bank’s routing number, your account number is private; that’s a key difference in routing vs. account numbers. Here are some other points about account numbers to know:
• Typically between nine and 12 digits, your account number acts as a road map of sorts for your bank, letting them know where to deposit or withdraw money, whether that’s a checking account or a savings account.
• If you have two different accounts at the same financial institution, you will have two different account numbers. The routing number for these accounts, however, will be the same.
• Because your account number can unlock access to the funds in your checking or savings account, it’s critical that you keep it safe.
Role of an Account Number in Transactions
Whether you are receiving a paycheck, making online purchases, or setting up autopay, your account number plays a key role. While routing numbers identify your bank, account numbers ensure that money is correctly credited to or debited from the right account.
Increase your savings
with a limited-time APY boost.*
When You’ll Need a Routing Number or Account Number
You’ll need to know your account number and routing number for a variety of everyday financial transactions. These may include:
• Setting up direct deposit of your paycheck
• Setting up autopay
• Setting up direct deposit of Social Security or other government benefits
• Paying a bill online
• Setting up autopay
• Check processing
• Sending or receiving a wire transfer
• Sending up a peer-to-peer payment app or service
• Transferring funds between accounts at different banks
• Making payments from your bank account by phone
• Ordering new checks
• Linking a budgeting app to your bank account
Finding Your Bank Routing and Account Numbers
If you need to find your routing and account numbers, you have several options:
Looking at a Check
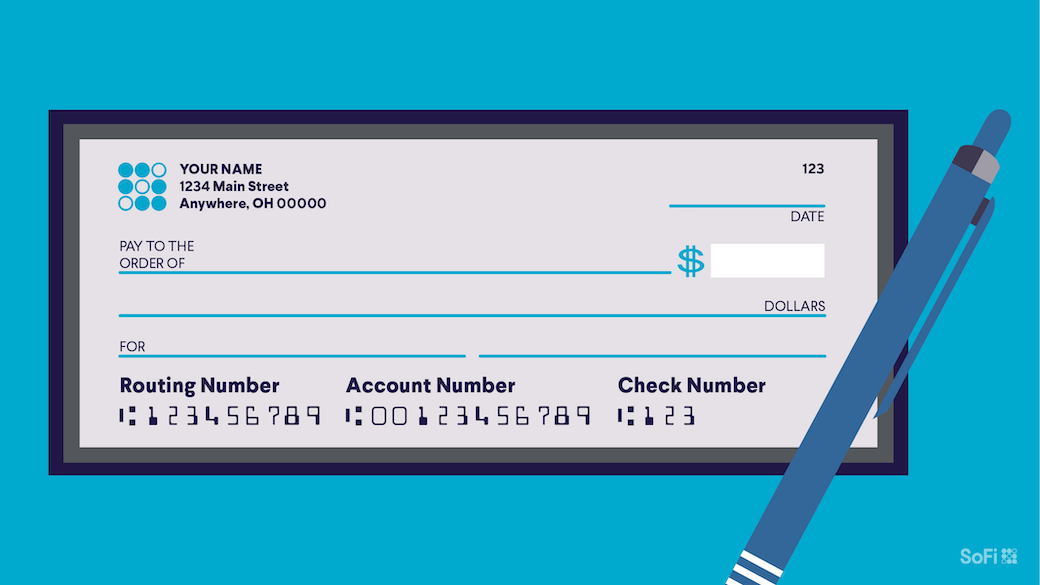
You can find your routing number and account number printed on the bottom of your checks.
You’ll see three groups of numbers (often separated by spaces and/or symbols). Typically, reading left to right, the first number (nine digits) is the routing number; the next group of numbers (usually nine to 12 digits) is the account number; the third is the actual check number.
Contacting Your Bank
If you need your bank routing and account numbers and don’t have access to a check, you can call your bank (or stop into a branch) and ask a customer service representative to provide you with the numbers. Since your account number is private information, you will likely have to provide identifying details to prove you are who you say you are to gain access to this number.
Note: If all you need is the routing number, you can easily find it on your bank’s website.
Accessing Your Online Account
If you log into your bank account online or in-app, you should be able to get your banking details. Your account number may be encrypted (meaning you can only see the last four digits). If that’s the case, you can typically get the full number by downloading a recent bank statement. Or, there may be a prompt you can click in order to see the full number.
Protecting Your Routing and Account Numbers
Although anyone can locate your bank’s routing number, your account number is not public information. Just like you are mindful about who sees your Social Security number, the same goes for your bank account number. You want to make sure that someone doesn’t use your bank account and routing number without authorization.
Tips for Keeping Your Banking Information Secure
Here are some ways to keep sensitive banking information safe:
• Avoid sharing your banking details unless necessary. To protect yourself from potential bank fraud, you generally don’t want to share your account number with any person or business unless you absolutely need to. Also wise: not sharing pictures of checks you’ve written on social media, even if it is for the first payment on your dream car.
• Store physical checks in a secure place. Since checks contain both your routing and account number, it’s a good idea to keep your checkbook tucked away in a safe place, not sitting out in the open. Also be sure to shred old checks and paper statements before throwing them away.
• Enable multi-factor authentication for online banking. Two- or three-factor authentication requires additional information beyond a password, such as a code sent to your mobile phone or a fingerprint scan, for account access. You’ll typically find this option inside the account settings.
• Regularly monitor your accounts. It’s a good idea to review your bank statements monthly and check your online banking once a week. This allows you to pick up on any suspicious transactions and nip any potential issues in the bud.
Recommended: How to Write a Check
What to Do if Your Information Is Compromised
If you suspect fraud or unauthorized access to your bank account:
• Contact your bank immediately. Call customer service and inform the representative of any unauthorized banking transactions as soon as you notice them.
• Change your login credentials: It’s a good idea to choose a new (unique) password for your bank account. Also consider setting up multi–factor authentication if you haven’t already.
• Review your recent transactions: Comb through recent activity on your bank account and make a list of any transactions you don’t recognize, noting the date and details. You’ll need this information to file a dispute with your bank.
• Consider placing a fraud alert on your credit report: You can contact any one of the three credit bureaus — Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion — to place a fraud alert on all three of your credit reports. A fraud alert is free and notifies creditors to take extra steps to verify your identity before extending credit.
The Takeaway
Your account and routing numbers work together to identify your account and ensure that your money gets transferred from the right place or that you receive funds intended for you. If you’re confused about routing vs. account numbers, the routing number indicates the bank where your account is held, while the account number identifies your specific account at that bank.
Knowing the difference between these numbers, where to locate them, and how to protect them is vital to managing your finances securely.
Interested in opening an online bank account? When you sign up for a SoFi Checking and Savings account with eligible direct deposit, you’ll get a competitive annual percentage yield (APY), pay zero account fees, and enjoy an array of rewards, such as access to the Allpoint Network of 55,000+ fee-free ATMs globally. Qualifying accounts can even access their paycheck up to two days early.
FAQ
Do you need both a routing and account number?
Typically, yes. Common transactions — like setting up direct deposits, making electronic payments, or transferring money between banks — require both a routing and account number. The routing number identifies your bank, while the account number specifies your individual account. Together, they ensure that funds are correctly transferred to or from the right institution and account.
That said, for some transactions (like in-branch deposits), just your account number may suffice, as the bank already knows its routing number.
What comes first on a check, a routing or account number?
Typically, when you look at the lower portion of a check (reading left to right), the routing number comes first, followed by the account number, and then the actual check number.
The routing number is a nine-digit code that identifies the bank, while the account number specifies your specific account within that bank. Checks are typically numbered to help with record-keeping.
Do I give my account number or routing number for a direct deposit?
For a direct deposit, you need to provide both your routing and account numbers. The routing number ensures the deposit is sent to the correct bank, while the account number directs the funds to your specific account. You may also be asked to provide a voided check.
What happens if I use the wrong routing or account number?
Using the wrong routing or account number can result in a failed transaction or funds being sent to the wrong account.
If your bank catches the mistake, it may reject the transaction. If your bank misses it and the account number belongs to someone else, the money could get deposited into the wrong account. If that occurs, you’ll want to contact your bank immediately to try to remedy the problem.
Are routing numbers the same across all branches of a bank?
Not necessarily. Smaller banks often have a single routing number for all branches. But if a bank has branches located in different states, routing numbers won’t be the same across all branches. Your routing number will be based on the branch where you first opened your account.
Photo credit: iStock/SeventyFour
SoFi Checking and Savings is offered through SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. The SoFi® Bank Debit Mastercard® is issued by SoFi Bank, N.A., pursuant to license by Mastercard International Incorporated and can be used everywhere Mastercard is accepted. Mastercard is a registered trademark, and the circles design is a trademark of Mastercard International Incorporated.
Annual percentage yield (APY) is variable and subject to change at any time. Rates are current as of 12/23/25. There is no minimum balance requirement. Fees may reduce earnings. Additional rates and information can be found at https://www.sofi.com/legal/banking-rate-sheet
Eligible Direct Deposit means a recurring deposit of regular income to an account holder’s SoFi Checking or Savings account, including payroll, pension, or government benefit payments (e.g., Social Security), made by the account holder’s employer, payroll or benefits provider or government agency (“Eligible Direct Deposit”) via the Automated Clearing House (“ACH”) Network every 31 calendar days.
Although we do our best to recognize all Eligible Direct Deposits, a small number of employers, payroll providers, benefits providers, or government agencies do not designate payments as direct deposit. To ensure you're earning the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit, we encourage you to check your APY Details page the day after your Eligible Direct Deposit posts to your SoFi account. If your APY is not showing as the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit, contact us at 855-456-7634 with the details of your Eligible Direct Deposit. As long as SoFi Bank can validate those details, you will start earning the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit from the date you contact SoFi for the next 31 calendar days. You will also be eligible for the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit on future Eligible Direct Deposits, as long as SoFi Bank can validate them.
Deposits that are not from an employer, payroll, or benefits provider or government agency, including but not limited to check deposits, peer-to-peer transfers (e.g., transfers from PayPal, Venmo, Wise, etc.), merchant transactions (e.g., transactions from PayPal, Stripe, Square, etc.), and bank ACH funds transfers and wire transfers from external accounts, or are non-recurring in nature (e.g., IRS tax refunds), do not constitute Eligible Direct Deposit activity. There is no minimum Eligible Direct Deposit amount required to qualify for the stated interest rate. SoFi Bank shall, in its sole discretion, assess each account holder's Eligible Direct Deposit activity to determine the applicability of rates and may request additional documentation for verification of eligibility.
See additional details at https://www.sofi.com/legal/banking-rate-sheet.
*Awards or rankings from NerdWallet are not indicative of future success or results. This award and its ratings are independently determined and awarded by their respective publications.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
We do not charge any account, service or maintenance fees for SoFi Checking and Savings. We do charge a transaction fee to process each outgoing wire transfer. SoFi does not charge a fee for incoming wire transfers, however the sending bank may charge a fee. Our fee policy is subject to change at any time. See the SoFi Bank Fee Sheet for details at sofi.com/legal/banking-fees/.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
SOBNK-Q125-084
Read more






